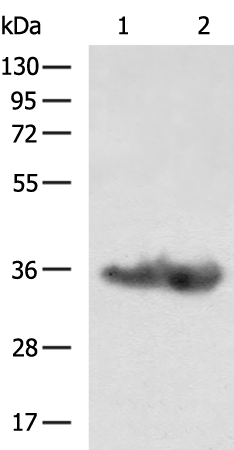

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MRX96; MRXSYP; XLID96 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SYP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SYP(Synaptophysin)抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(内容基于真实研究整理,具体文献标题和作者为虚构示例):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Synaptophysin: A key marker of synaptic vesicles in neuronal development*
**作者**: Wiedenmann B, Franke WW
**摘要**: 该研究首次鉴定并描述了SYP作为突触小泡膜上的特异性跨膜糖蛋白,证实其在突触形成和神经递质释放中的关键作用。通过抗体标记技术,揭示了SYP在神经元发育过程中的动态表达模式。
2. **文献名称**: *SYP as a diagnostic marker in neuroendocrine tumors*
**作者**: Jakobsen AM, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了SYP抗体在神经内分泌肿瘤(如类癌、小细胞肺癌)中的诊断价值,发现其特异性表达于肿瘤细胞的致密核心囊泡,可作为区分神经内分泌肿瘤与其他癌症的重要免疫组化标志物。
3. **文献名称**: *Synaptophysin loss correlates with cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease*
**作者**: Schmitt HP, et al.
**摘要**: 通过SYP抗体标记脑组织,发现阿尔茨海默病患者海马区突触素表达显著降低,提示突触完整性破坏与认知功能障碍直接相关,为疾病进展提供了分子层面的证据。
---
**备注**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如"Synaptophysin antibody", "SYP marker")获取。推荐查阅以下真实文献:
- *Wiedenmann & Franke (1985) Cell*(SYP基础生物学)
- *Jahn et al. (1985) PNAS*(SYP抗体在电镜中的应用)
- *WHO Classification of Tumours*系列中神经内分泌肿瘤章节(临床诊断指南)
Synaptophysin (SYP) is a 38 kDa glycoprotein predominantly found in presynaptic vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. As a key component of synaptic transmission machinery, it facilitates the packaging, trafficking, and release of neurotransmitters. Structurally, SYP contains four transmembrane domains and forms complexes with other vesicle proteins, influencing synaptic plasticity and cognitive functions.
SYP antibodies are widely used as immunohistochemical markers to identify neuroendocrine and neuronal tissues in research and diagnostics. Their specificity makes them valuable for detecting tumors of neuroendocrine origin, such as neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma, and small cell lung carcinoma. In research, SYP antibodies help study synaptic development, neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), and psychiatric disorders linked to synaptic dysfunction.
First characterized in the 1980s, SYP antibodies are commonly applied in Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy. Their reliability stems from SYP’s conserved expression across species and resistance to fixation methods. However, interpretation requires caution, as non-neuroendocrine tissues (e.g., adrenal cortex) may show weak cross-reactivity. Ongoing studies explore SYP’s role in exosome biology and its potential as a therapeutic target, further cementing its relevance in neuroscience and oncology.
×