| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
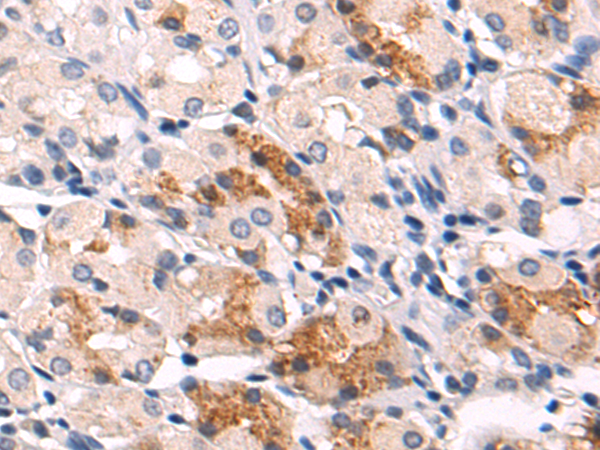
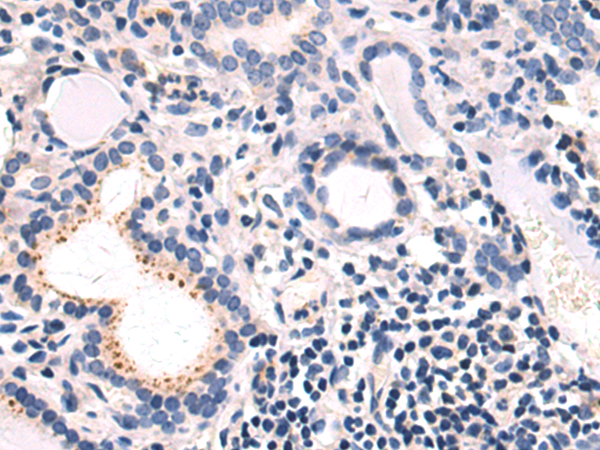
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DUBA8; OTUD2; PRO0907 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human YOD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇与YOD1抗体相关的参考文献及简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"YOD1/TRAF6 association balances p62-dependent IL-1 signaling to NF-κB"*
**作者**: Hrdinka, M., et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过YOD1抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现YOD1与TRAF6相互作用,调控p62依赖的IL-1信号通路,抑制过度NF-κB激活,揭示其在炎症反应中的负反馈机制。
2. **文献名称**: *"YOD1 deubiquitinates NEMO/IKKγ to coordinate NF-κB activation in response to genotoxic stress"*
**作者**: Schimmack, G., et al.
**摘要**: 利用YOD1特异性抗体进行功能研究,发现YOD1通过去泛素化NEMO蛋白,调控DNA损伤诱导的NF-κB信号通路,维持细胞在基因毒性压力下的存活。
3. **文献名称**: *"The deubiquitinase YOD1 regulates cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress"*
**作者**: Tsuchiya, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 通过YOD1抗体检测其在心脏组织中的表达,证明YOD1通过缓解内质网应激抑制病理性心脏肥厚,为治疗心力衰竭提供新靶点。
4. **文献名称**: *"YOD1 promotes neuronal degeneration through inhibiting autophagy flux in Parkinson’s disease models"*
**作者**: Liu, J., et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用YOD1抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现YOD1在帕金森模型中通过去泛素化Beclin-1抑制自噬流,加剧多巴胺能神经元退化。
---
以上文献均涉及YOD1抗体的实验应用,涵盖炎症、神经退行性疾病、心脏疾病及DNA损伤修复等领域。如需具体文献来源(期刊、年份等),可进一步提供数据库检索支持。
YOD1 (also known as OTUD2) is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) belonging to the ovarian tumor (OTU) domain-containing protein family. It plays a critical role in regulating cellular protein homeostasis by cleaving ubiquitin chains attached to substrate proteins, thereby influencing their stability, localization, or activity. YOD1 is particularly implicated in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), a quality control pathway that identifies and removes misfolded proteins from the ER. Through its interaction with key ERAD components like VCP/p97. YOD1 facilitates the retrotranslocation of ubiquitinated substrates for proteasomal degradation. Dysregulation of YOD1 has been linked to various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, and immune system abnormalities, highlighting its importance in cellular stress responses and survival.
YOD1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in these pathways. They enable researchers to detect YOD1 protein levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunoprecipitation. Specific antibodies can distinguish between different post-translational modifications or conformational states of YOD1. providing insights into its regulatory mechanisms. Commercially available YOD1 antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting unique epitopes within the N-terminal OTU domain or C-terminal regions. Validation of these antibodies includes testing for specificity using knockout cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown. As research on YOD1 expands, these antibodies remain vital for exploring its therapeutic potential in diseases linked to protein misfolding or ubiquitination defects.
×