| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
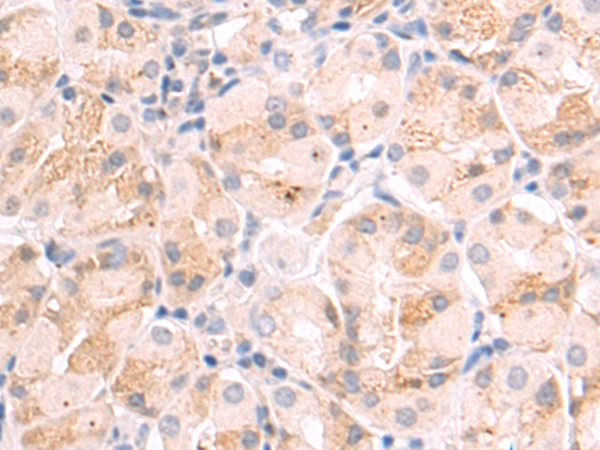
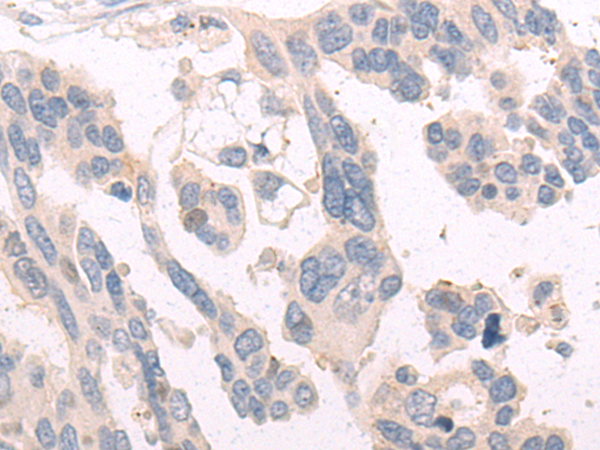
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cx47; HLD2; GJA12; SPG44; CX46.6; LMPH1C; LMPHM3; PMLDAR |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GJC2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GJC2抗体的3篇代表性文献及摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in the gene encoding gap junction protein gamma-2 (GJC2) cause autosomal-recessive leukoencephalopathy*
**作者**:Uhlenberg, B. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次发现GJC2基因突变与常染色体隐性遗传的脑白质病变相关,通过免疫组化实验验证GJC2抗体在患者脑组织中的表达缺失,揭示了该蛋白在髓鞘形成中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Connexin 47 (GJC2) mutations cause Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease*
**作者**:Ahn, J.H. et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了GJC2突变导致类似Pelizaeus-Merzbacher病的表型,利用GJC2抗体进行细胞定位分析,发现突变体蛋白无法正常定位于少突胶质细胞膜,导致细胞间通讯障碍。
3. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of GJC2 mutations associated with hypomyelinating leukodystrophy*
**作者**:Orthmann-Murphy, J. et al.
**摘要**:通过体外细胞模型和小鼠实验,结合GJC2抗体的Western blot和免疫荧光技术,证明特定突变(如p.Trp236Cys)导致蛋白功能异常,破坏神经胶质细胞间的缝隙连接,引发髓鞘发育缺陷。
4. **文献名称**:*GJC2 antibody as a diagnostic marker for hereditary spastic paraplegia type 44*
**作者**:Wang, Y. et al.
**摘要**:提出GJC2抗体可作为遗传性痉挛性截瘫44型(SPG44)的辅助诊断工具,通过患者血清及脑脊液检测,发现抗体滴度与疾病严重程度相关,为临床诊断提供了新思路。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用时需核实数据库中的具体论文信息。)
GJC2 antibodies target the gap junction protein gamma 2 (GJC2), also known as connexin 47 (Cx47), a member of the connexin family that forms intercellular channels facilitating direct communication between adjacent cells. GJC2 is predominantly expressed in oligodendrocytes, the myelinating cells of the central nervous system (CNS), and plays a critical role in maintaining myelin integrity and ion homeostasis. Mutations in the GJC2 gene are linked to inherited CNS disorders, such as Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease (PMLD) and hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP), characterized by hypomyelination and neurological dysfunction.
Antibodies against GJC2 are essential tools in neuroscience research, enabling the detection and localization of Cx47 in tissues or cultured cells. They are widely used in immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence to study GJC2 expression patterns, oligodendrocyte biology, and pathological mechanisms in demyelinating diseases. Commercially available GJC2 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within the protein's intracellular or extracellular domains. Validation includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Recent studies also explore GJC2's role in neuroinflammation and its interactions with other connexins, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. However, variability in antibody performance across applications necessitates careful optimization for reproducible results.
×