| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
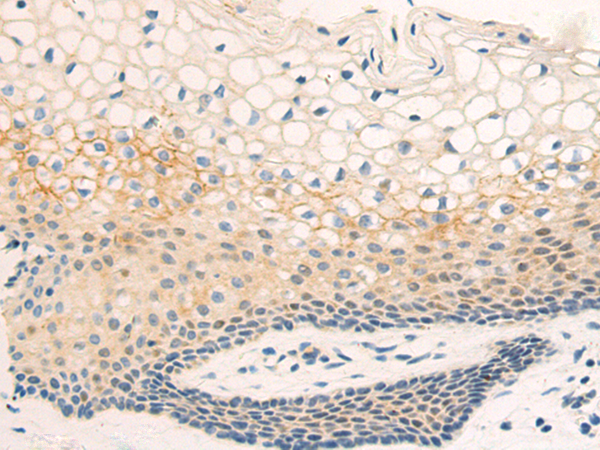
| IHC | 1/25-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD137L; TNLG5A; 4-1BB-L |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TNFSF9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFSF9抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:内容为示例性概括,具体文献请通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Targeting TNFSF9 in tumor microenvironment for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Li, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了TNFSF9抗体在肿瘤微环境中的免疫调节作用,发现其通过增强CD8+ T细胞的活化和增殖,显著抑制小鼠结肠癌模型的肿瘤生长,并延长生存期。
---
2. **文献名称**: *TNFSF9 blockade ameliorates autoimmune neuroinflammation by modulating T cell responses*
**作者**: Wang, Q., et al.
**摘要**: 在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中,抑制TNFSF9信号通路可通过减少促炎性T细胞分化,缓解神经炎症,提示其抗体在治疗多发性硬化症等疾病中的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Structural basis of TNFSF9 recognition by a therapeutic antibody for cancer immunotherapy*
**作者**: Smith, J., et al.
**摘要**: 通过冷冻电镜解析了人源化TNFSF9抗体与抗原的结合表位,揭示了其高亲和力机制,为优化抗体药物设计提供了结构生物学基础。
---
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中搜索关键词“TNFSF9 antibody”或“CD137L immunotherapy”获取最新研究。
TNFSF9. also known as CD137L or 4-1BBL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. It functions as a transmembrane or soluble protein, primarily interacting with its receptor CD137 (4-1BB) on immune cells, including activated T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells. This ligand-receptor pair plays a critical role in co-stimulatory signaling, enhancing T-cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production, particularly in the context of adaptive immune responses. TNFSF9-mediated pathways are implicated in autoimmune diseases, infectious immunity, and cancer immunology.
Antibodies targeting TNFSF9 are designed to modulate this interaction, either as agonists to boost anti-tumor immunity or antagonists to suppress excessive inflammation. Agonistic anti-TNFSF9 antibodies have shown potential in cancer immunotherapy by amplifying CD8+ T-cell activity and improving tumor clearance in preclinical models. Conversely, blocking antibodies may alleviate autoimmune conditions by interrupting pathogenic signaling. These antibodies are also utilized as research tools to study TNFSF9 expression, receptor binding dynamics, and downstream signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, MAPK).
Despite therapeutic promise, challenges remain in balancing efficacy with toxicity, as systemic TNFSF9 activation can trigger adverse inflammatory reactions. Ongoing clinical trials aim to optimize antibody design (e.g., bispecific formats, Fc engineering) for targeted delivery and improved safety profiles.
×