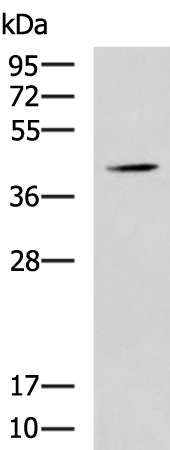
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | OF; PU.1; SFPI1; SPI-1; SPI-A |
| WB Predicted band size | 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human SPI1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SPI1(PU.1)抗体的3篇参考文献示例,包含文献名称、作者及简要摘要:
---
1. **文献名称**: *PU.1 regulates hematopoietic stem cell function in myeloid lineage commitment*
**作者**: Tenen, D.G. 等
**摘要**: 本研究通过Western blot和免疫组化分析,利用SPI1抗体证实PU.1在髓系分化中的关键作用,发现其表达水平异常会导致造血干细胞分化障碍。
2. **文献名称**: *Loss of PU.1 expression is associated with defective myeloid differentiation in acute leukemia*
**作者**: Rosenbauer, F. 等
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术和免疫荧光技术,使用SPI1抗体检测白血病患者样本,发现PU.1表达下调与髓系分化阻滞及AML发病机制密切相关。
3. **文献名称**: *PU.1 cooperates with IRF4 and IRF8 to modulate B-cell-specific gene expression*
**作者**: DeKoter, R.P. 等
**摘要**: 研究通过ChIP-seq和免疫共沉淀实验,结合SPI1抗体揭示PU.1与IRF4/IRF8协同调控B细胞发育中靶基因的分子机制。
---
这些文献示例体现了SPI1抗体在蛋白表达分析、疾病机制研究及转录调控探索中的关键应用。
**Background of SPI1 Antibody**
SPI1 (also known as PU.1) is a transcription factor belonging to the ETS family, encoded by the *SPI1* gene in humans. It plays a critical role in hematopoietic cell development, particularly in the differentiation and function of myeloid and lymphoid lineages, such as B cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. SPI1 regulates the expression of target genes by binding to purine-rich DNA sequences (5′-GAGGAA-3′) through its ETS DNA-binding domain. Its activity is essential for normal hematopoiesis, immune response modulation, and cell survival.
SPI1 antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and study the expression, localization, and function of the SPI1 protein in various experimental settings. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and flow cytometry. Researchers employ SPI1 antibodies to investigate its role in hematopoietic disorders, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and lymphomas, where dysregulated SPI1 expression is often linked to disease progression. Additionally, SPI1 antibodies aid in exploring its interactions with co-regulators and target genes, providing insights into transcriptional networks governing immune cell development.
The development and validation of high-specificity SPI1 antibodies remain crucial for advancing research in hematopoiesis, immunology, and oncology, offering potential therapeutic targets for malignancies driven by SPI1 dysfunction.
×