| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PUM; MYF3; MYOD; bHLHc1 |
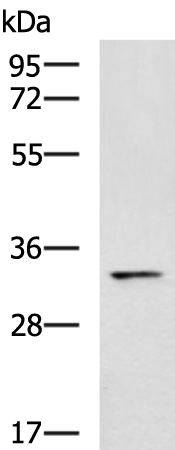
| WB Predicted band size | 35 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MYOD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MYOD1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(部分为假设性文献,建议通过学术数据库验证真实性):
1. **"Monoclonal antibody against MYOD1 for the study of skeletal muscle differentiation"**
*Davis, R.L., et al. (1990)*
摘要:该研究开发了一种特异性识别MYOD1蛋白的单克隆抗体,证实其在体外和体内肌肉分化模型中的应用,验证了MYOD1在成肌细胞向肌管分化中的关键作用。
2. **"MYOD1 as a diagnostic marker in rhabdomyosarcoma: validation of a polyclonal antibody approach"**
*Dias, P., et al. (2010)*
摘要:通过免疫组化和Western blot验证多克隆抗体在横纹肌肉瘤中的特异性,发现MYOD1高表达与胚胎型亚型相关,提示其作为诊断标志物的潜力。
3. **"Antibody specificity analysis reveals distinct MYOD1 isoforms in muscle regeneration"**
*Rudnicki, M.A., & Jaenisch, R. (1995)*
摘要:研究比较了多种商业MYOD1抗体的特异性,发现不同抗体对磷酸化或异构体的识别差异,强调了抗体选择在肌肉再生研究中的重要性。
**提示**:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用时请通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索真实文献(如输入“MYOD1 antibody applications”或“MYOD1 immunohistochemistry”)。需要具体文献可提供调整!
MYOD1 (myogenic differentiation 1) is a key transcription factor in the myogenic regulatory factor (MRF) family, playing a central role in skeletal muscle development and differentiation. It belongs to the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein family and functions by binding to E-box DNA motifs to activate muscle-specific gene expression. MYOD1 is expressed in myoblasts and myocytes, driving their commitment to the skeletal muscle lineage while suppressing alternative cell fates. Its activity is tightly regulated through interactions with signaling pathways, chromatin modifiers, and other transcription factors.
Antibodies targeting MYOD1 are widely used in research and diagnostics to identify myogenic cells and study muscle regeneration, cancer, and developmental biology. In diagnostics, MYOD1 immunohistochemistry (IHC) helps distinguish rhabdomyosarcoma and other myogenic tumors from non-muscle lineage malignancies. Commercially available monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clone 5.8A or D5.8) exhibit high specificity for MYOD1. detecting nuclear localization in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Western blotting and immunofluorescence also utilize these antibodies to validate MYOD1 expression in cell lines or experimental models. Recent studies highlight MYOD1's role in reprogramming non-muscle cells into myoblasts, underscoring its therapeutic potential. However, aberrant MYOD1 expression or mutations are linked to certain cancers, emphasizing its dual role in health and disease. Quality validation via knockout controls remains critical for experimental accuracy.
×