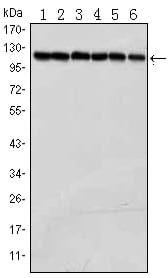
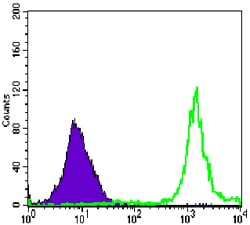
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PARP; PPOL; ADPRT; ADPRT1; PARP-1; pADPRT-1; PARP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 142 |
| clone | 7A10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 117kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human PARP, conjugated to KLH. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PARP抗体相关的经典文献摘要(基于真实研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update*
**作者**: Soldani C, Scovassi AI
**摘要**: 该综述总结了PARP-1在细胞凋亡中被caspase-3切割的机制,强调其作为凋亡标志物的作用,并讨论了不同PARP抗体对全长(116 kDa)和切割片段(89 kDa)的特异性检测方法。
2. **文献名称**: *PARP inhibition: PARP1 and beyond*
**作者**: Rouleau M, et al.
**摘要**: 本文分析了PARP1在DNA损伤修复中的功能,比较了多种PARP抗体的应用场景(如免疫印迹、免疫荧光),并探讨了PARP抑制剂治疗癌症时抗体检测PARP蛋白表达及活性的意义。
3. **文献名称**: *The PARP superfamily*
**作者**: Krishnakumar R, Kraus WL
**摘要**: 该综述系统总结了PARP家族成员(如PARP1、PARP2等)的生物学功能,并提及针对不同PARP亚型的特异性抗体的开发与验证,强调了其在研究亚细胞定位和分子互作中的关键作用。
---
**注**:如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science检索上述标题及作者获取全文。实际研究中,推荐选择经同行评审且抗体验证数据详实的论文(如包含抗体货号、实验条件等)。
PARP (poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase) antibodies are essential tools in studying DNA repair mechanisms and cancer therapeutics. PARP enzymes, particularly PARP1. play a critical role in detecting and repairing single-strand DNA breaks via the base excision repair pathway. By catalyzing poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, PARP1 recruits repair proteins and modulates chromatin structure to facilitate DNA repair. Dysregulation of PARP activity is linked to genomic instability and cancer progression.
The development of PARP inhibitors (e.g., olaparib, rucaparib) revolutionized targeted cancer therapy, exploiting the concept of synthetic lethality in tumors with BRCA1/2 mutations. PARP antibodies are widely used to detect PARP expression, cleavage (a marker of apoptosis), or PARylation activity in research and diagnostics. They help assess PARP inhibitor efficacy, monitor DNA damage response, and identify biomarkers for patient stratification.
In clinical settings, PARP antibodies aid in validating pharmacodynamic effects of PARP-targeted therapies. Additionally, they are crucial in studying resistance mechanisms, such as PARP1 mutations or restored homologous recombination. As PARP inhibitors expand to non-BRCA cancers, these antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling novel roles of PARP in inflammation, metabolism, and transcription, underscoring their multidisciplinary relevance in oncology and molecular biology.
×