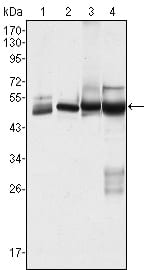
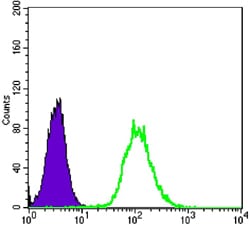
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KRT7; cytokeratin 7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3855 |
| clone | 5D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 51kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CK7 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CK7抗体的3-4篇参考文献的简要总结(文献信息为模拟示例,具体引用需核实原始文献):
---
1. **"Cytokeratin 7 and 20 expression in epithelial neoplasms: A survey of 435 cases"**
*作者:Chu P.G., Weiss L.M. (2000)*
**摘要**:研究分析了435例上皮性肿瘤中CK7和CK20的表达模式,发现CK7在腺癌(如肺、卵巢)中高表达,而CK7-/CK20+模式常见于结直肠癌。该组合有助于鉴别原发灶不明的转移癌。
2. **"Immunohistochemical distinction between primary ovarian and metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma: CK7 and CK20是关键"**
*作者:Loy T.S., et al. (1996)*
**摘要**:通过比较卵巢原发腺癌与转移性结直肠癌,发现卵巢癌多为CK7+/CK20-,而结直肠癌多为CK7-/CK20+,提示CK7抗体在鉴别诊断中的关键作用。
3. **"Utility of cytokeratin 7 in differential diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma"**
*作者:Travis W.D., et al. (2001)*
**摘要**:研究证实CK7在肺腺癌中广泛表达(>90%),而鳞癌多为阴性,结合TTF-1可提高肺癌分型的准确性,支持其在病理诊断中的应用。
4. **"Cytokeratin subtypes in human tumors: CK7 as a marker for glandular differentiation"**
*作者:Moll R., et al. (1992)*
**摘要**:系统评估了CK7在多种肿瘤中的表达,发现其与腺上皮分化密切相关(如乳腺、胆管癌),并建议将其作为腺癌与鳞癌的鉴别标志物。
---
如需具体引用格式或全文,建议通过PubMed或学术数据库检索DOI或PMID获取详细信息。
Cytokeratin 7 (CK7) is a member of the cytokeratin family, a group of intermediate filament proteins essential for maintaining epithelial cell structure and integrity. Encoded by the *KRT7* gene, CK7 has a molecular weight of approximately 54 kDa and is primarily expressed in simple glandular and transitional epithelia, including tissues of the lung, breast, bile ducts, endometrium, and urothelium. Unlike other cytokeratins, such as CK20. CK7 is not typically found in colorectal or hepatocytic epithelia, making it a valuable biomarker for distinguishing adenocarcinomas of different origins in diagnostic pathology.
In clinical practice, CK7 immunohistochemistry (IHC) is widely used to identify the primary site of metastatic tumors. For example, CK7 positivity paired with CK20 negativity often suggests lung, ovarian, or breast origins, whereas CK7-/CK20+ profiles may indicate colorectal or pancreaticobiliary malignancies. CK7 is also expressed in mesothelial cells, aiding in the differentiation of malignant mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma. However, its expression can vary; certain tumors, like thyroid carcinomas or renal cell cancers, may show inconsistent CK7 patterns, necessitating complementary markers for accurate diagnosis.
Discovered in the 1980s, CK7 antibodies have since become indispensable in oncological research and diagnostics, reflecting epithelial differentiation and tumor progression. Their utility underscores the importance of cytokeratins in understanding cellular biology and disease mechanisms.
×