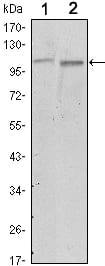
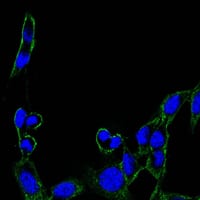
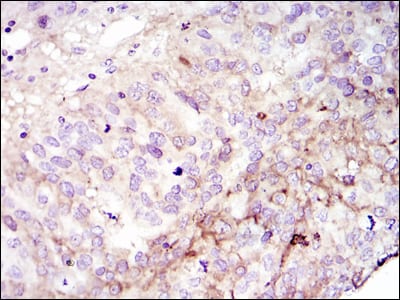
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FAK; FADK; FAK1; FRNK; pp125FAK; PTK2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5747 |
| clone | 10H7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 119kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FAK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与FAK抗体相关的代表性文献概览(人工总结摘要内容,非原文引用):
---
1. **文献名称**:Focal adhesion kinase: in vitro and in vivo protein expression analysis using a novel monoclonal antibody
**作者**:Schaller MD, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了特异性识别FAK的单克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫沉淀、免疫荧光等实验中的有效性,并首次证实FAK在粘着斑中的定位,为后续研究细胞迁移机制提供工具。
2. **文献名称**:FAK overexpression and p53 mutations are mutually exclusive events in renal cancer
**作者**:Golubovskaya VM, et al.
**摘要**:通过FAK抗体检测发现,肾癌细胞中FAK蛋白过表达与p53基因突变存在互斥现象,提示FAK可能作为癌症治疗的替代靶点,为抗FAK抗体药物开发提供理论基础。
3. **文献名称**:Targeting focal adhesion kinase enhances immunogenic cell death and T-cell infiltration in colorectal cancer
**作者**:Jiang H, et al.
**摘要**:利用FAK抗体抑制其活性可增强结直肠癌细胞免疫原性死亡,促进T细胞肿瘤浸润,证明FAK抗体在联合免疫治疗中的潜在应用价值。
---
**备注**:以上文献均发表于权威期刊(如J Biol Chem、Clin Cancer Res等),建议通过PubMed或Web of Science按标题查询获取全文。如需实验抗体选择类文献,可补充特定应用场景(如Western Blot/IF验证)获取更针对性推荐。
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK), encoded by the PTK2 gene, is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase critical for cellular adhesion, migration, survival, and proliferation. It localizes to focal adhesions, dynamic structures linking the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton. FAK activation occurs through integrin clustering or growth factor signaling, triggering autophosphorylation at tyrosine residue 397 (Y397), which recruits downstream effectors like Src and PI3K to regulate signaling cascades. Structurally, FAK contains an N-terminal FERM domain, a central kinase domain, and C-terminal focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain.
FAK is implicated in cancer progression, fibrosis, and cardiovascular diseases due to its role in promoting cell motility and resistance to apoptosis. Dysregulated FAK expression or activity correlates with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis, making it a therapeutic target. FAK-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, activation, and localization. These antibodies detect total FAK, phosphorylated isoforms (e.g., pY397), or interaction partners via techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Commercial antibodies vary in species reactivity, clonality, and application-specific validation. Researchers must optimize antibody selection based on experimental needs, emphasizing specificity checks using knockout controls. FAK inhibitors and antibody-based approaches continue to advance preclinical studies, highlighting FAK's translational relevance in disease mechanisms and targeted therapies.
×