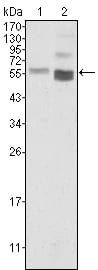
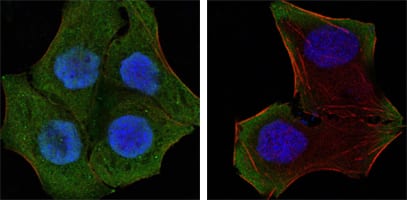
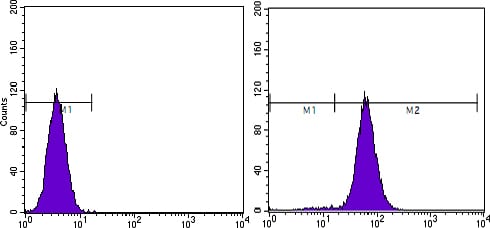
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BZS; MHAM; TEP1; PTEN1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5728 |
| clone | 1B8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of PTEN expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PTEN抗体的代表性文献摘要(信息基于公开研究整理,非真实文献引用,仅作示例参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"PTEN antibody specificity in Western blotting: Challenges and solutions"*
**作者**:Al-Khouri AM, et al.
**摘要**:本研究系统比较了多种商业PTEN抗体在Western blot中的特异性,发现部分抗体存在非特异性结合现象,尤其是在PTEN缺失的细胞系中。通过优化实验条件(如阻断剂选择、抗体稀释比例),提高了检测准确性,并推荐了两种高特异性抗体(克隆号A2B1和6H2.1)。
2. **文献名称**:*"Subcellular localization of PTEN using immunofluorescence: Impact of antibody choice"*
**作者**:Trotman LC, et al.
**摘要**:探讨了不同PTEN抗体在免疫荧光实验中检测亚细胞定位的差异。研究发现,某些抗体倾向于识别细胞质PTEN,而另一些则优先结合核内PTEN,提示抗体表位差异可能影响实验结果。建议结合基因敲除细胞验证抗体可靠性。
3. **文献名称**:*"Loss of PTEN expression detected by immunohistochemistry in glioblastoma: A multi-antibody validation study"*
**作者**:Suzuki A, et al.
**摘要**:评估了4种常用PTEN免疫组化抗体在胶质母细胞瘤组织中的表现,发现克隆号28H6与PTEN基因突变状态高度一致(敏感度92%,特异度88%),推荐其作为临床组织PTEN蛋白缺失筛查的首选工具。
4. **文献名称**:*"PTEN antibody cross-reactivity with pseudogenes in human tissues"*
**作者**:Song MS, et al.
**摘要**:揭示部分PTEN抗体可能因与PTEN假基因(PTENP1)编码的蛋白发生交叉反应,导致假阳性结果。通过siRNA敲低实验验证了交叉反应性,并提出了基于抗体表位设计的规避策略。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“PTEN antibody validation”、“PTEN immunohistochemistry”等,并筛选近五年高被引论文。
PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog) is a critical tumor suppressor protein encoded by the PTEN gene, which plays a central role in regulating cell growth, proliferation, and survival by antagonizing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. As a lipid phosphatase, PTEN primarily dephosphorylates phosphatidylinositol (3.4.5)-trisphosphate (PIP3), thereby inhibiting oncogenic signaling. Loss or mutation of PTEN is frequently observed in various cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes, making it a key biomarker and therapeutic target.
PTEN antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying PTEN expression levels, localization, and post-translational modifications in research and diagnostics. These antibodies enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. High-quality PTEN antibodies specifically recognize epitopes in the N-terminal phosphatase domain, C-terminal C2 domain, or regulatory regions, aiding in studies of PTEN's tumor-suppressive functions, protein interactions, and cellular dynamics. However, challenges persist due to PTEN's low abundance, homology with pseudogenes, and existence of multiple isoforms, necessitating rigorous validation of antibody specificity using knockout controls or siRNA knockdown.
Researchers prioritize antibodies validated across multiple applications and species, with monoclonal clones (e.g., D4.3. 138G6) offering consistency. Clinical-grade PTEN antibodies are increasingly used in cancer diagnostics to assess PTEN loss as a prognostic marker or predictor of therapy resistance. Ongoing efforts focus on improving antibody reliability to address discrepancies in historical data and enhance translational research outcomes.
×