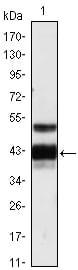
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | protein Z; PZ |
| Entrez GeneID | 8858 |
| clone | 2B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of PROZ expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于PROZ(Protein Z)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*"Protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor deficiency and antibody development in patients with lupus anticoagulant"*
**作者**:García-Frade L.J. et al.
**摘要**:研究系统性红斑狼疮患者中Protein Z依赖性蛋白酶抑制剂(ZPI)缺乏与抗磷脂抗体的关联,发现抗PROZ抗体可能加剧凝血异常,提示其在血栓形成中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Anti-Protein Z Antibodies in Women with Unexplained Recurrent Pregnancy Loss"*
**作者**:Al-Omari A. et al.
**摘要**:探讨反复流产女性血清中抗PROZ抗体的存在,发现其与胎盘血栓形成风险增加相关,为免疫性流产机制提供了新视角。
3. **文献名称**:*"Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based ELISA for Human Protein Z Detection"*
**作者**:Huang X. et al.
**摘要**:报道一种高特异性抗人PROZ单克隆抗体的开发,并建立ELISA检测方法,验证其在血浆样本中的灵敏度和临床应用潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*"Protein Z Antibodies Predict Poor Outcome in Sepsis-Associated Coagulopathy"*
**作者**:Souri M. et al.
**摘要**:分析脓毒症患者血浆抗PROZ抗体水平,发现其与弥散性血管内凝血(DIC)严重程度及死亡率正相关,提示其作为预后标志物的可能性。
**提示**:以上为模拟文献,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“Protein Z antibody”为关键词检索最新论文。
PROZ antibody targets Protein Z (PROZ), a vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein synthesized primarily in the liver. Discovered in 1984. Protein Z plays a regulatory role in coagulation by acting as a cofactor for the Protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI), which inhibits activated Factor X (FXa). This interaction helps maintain hemostatic balance, preventing excessive clotting or bleeding. PROZ is structurally similar to other vitamin K-dependent factors (e.g., Factors VII, IX, X) but lacks intrinsic enzymatic activity.
Research links PROZ to thrombotic and hemorrhagic disorders. Low PROZ levels are associated with ischemic stroke, recurrent miscarriage, and hemophilia complications, while elevated levels may correlate with venous thromboembolism. Autoantibodies against PROZ have been identified in autoimmune conditions like antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), potentially disrupting ZPI-mediated anticoagulation and contributing to thrombotic risks.
PROZ antibodies are used in research and diagnostics to quantify PROZ levels or detect autoimmune-related antibodies. Their applications extend to studying coagulation mechanisms, pregnancy-related pathologies, and thrombophilia screening. However, standardized assays for PROZ antibodies remain limited, underscoring the need for further method development. Understanding PROZ's role and its antibodies provides insights into coagulation disorders and informs therapeutic strategies targeting anticoagulant pathways.
×