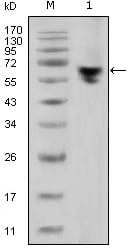
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| clone | 2E4 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified fusion protein with human IgG (Fc Specific) tag. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于人IgG Fc特异性抗体的经典文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Structural analysis of human IgG-Fc glycoforms reveals a correlation between glycosylation and structural integrity"*
**作者**: Sondermann, P., et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了人IgG Fc区域不同糖基化形式的结构,揭示了糖链修饰对Fc构象稳定性的影响及其与Fcγ受体结合的潜在调控机制。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Specificity and affinity of human Fcγ receptors and their polymorphic variants for human IgG subclasses"*
**作者**: Bruhns, P., et al.
**摘要**: 系统比较了人Fcγ受体(FcγR)家族对不同IgG亚类(IgG1-4)的Fc区域结合特异性,为抗Fc抗体的开发及治疗性抗体的优化提供了功能学依据。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Glycosylation of antibody Fc: a molecular basis for selection of anti-inflammatory IgG glycoforms"*
**作者**: Jefferis, R.
**摘要**: 综述了IgG Fc糖基化修饰(如岩藻糖、半乳糖)对抗体效应功能(如ADCC、CDC)的调控作用,强调糖工程在开发Fc特异性抗体中的关键意义。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Engineered Fc variants with enhanced FcγR binding and effector functions"*
**作者**: Shields, R.L., et al.
**摘要**: 通过定向突变技术改造IgG Fc区域,获得与激活型FcγR(如FcγRIIIa)结合增强的变体,为癌症免疫治疗中抗体药物的Fc功能优化提供了策略。
---
这些文献涵盖了Fc结构、受体互作、糖基化调控及工程改造等核心方向,可作为研究Fc特异性抗体的基础参考。
Human IgG (Fc-specific) antibodies are immunoglobulins designed to selectively target the Fc (fragment crystallizable) region of human IgG molecules. The Fc region, located in the heavy-chain constant domain of IgG, plays a critical role in mediating immune effector functions such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement activation, and interactions with Fc receptors (FcγRs) on immune cells. Fc-specific antibodies avoid binding to the Fab (antigen-binding fragment) region, ensuring specificity for conserved Fc epitopes across IgG subclasses (IgG1-4). This specificity is essential in applications requiring isolation, detection, or functional modulation of IgG without interfering with antigen recognition.
These antibodies are widely used in research, diagnostics, and therapeutics. In immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, Western blot), they enable IgG quantification or purification while minimizing cross-reactivity with other antibody isotypes. In therapeutic settings, Fc-specific reagents help study monoclonal antibody pharmacokinetics or engineer IgG molecules with tailored effector functions. They are also vital in autoimmune disease research, where Fc-mediated pathways drive pathologies like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Fc-specific antibodies are typically generated in animals (e.g., rabbits, goats) by immunizing with purified human IgG Fc fragments. Monoclonal variants offer high reproducibility, while polyclonal versions provide broad Fc subclass recognition. Their utility underscores the importance of the Fc domain in both physiological immunity and biotechnological applications.
×