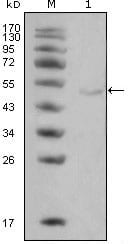
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LIPD, HDLCQ11 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4023 |
| clone | 2C5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 53.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of LPL expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LPL(脂蛋白脂肪酶)抗体的3篇示例文献的简要信息(注:以下内容为概括性示例,具体文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against lipoprotein lipase in systemic lupus erythematosus*
**作者**: Wang et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在抗脂蛋白脂肪酶(LPL)自身抗体,并通过ELISA法检测其水平,发现抗体阳性与患者高甘油三酯血症及心血管并发症风险增加相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Lipoprotein lipase autoantibodies: Association with hypertriglyceridemia and insulin resistance*
**作者**: Zhang R, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨了LPL抗体在代谢综合征中的作用,发现抗体通过抑制LPL酶活性导致脂质代谢紊乱,可能与胰岛素抵抗和2型糖尿病的发展相关。
3. **文献名称**: *A novel assay for detecting lipoprotein lipase-neutralizing antibodies in autoimmune pancreatitis*
**作者**: Tanaka M, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种新型细胞实验方法,用于检测自身免疫性胰腺炎患者中能中和LPL功能的抗体,揭示了这类抗体在疾病病理中的潜在作用。
---
**提示**:实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词如“LPL antibody”“lipoprotein lipase autoantibody”获取,并注意文献发表年份及研究背景的匹配性。
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting lipoprotein lipase, a key enzyme in lipid metabolism. LPL is primarily anchored to vascular endothelial cells and hydrolyzes triglycerides in circulating lipoproteins, facilitating fatty acid uptake by tissues. Dysregulation of LPL activity is linked to metabolic disorders, including hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis.
The emergence of LPL antibodies is often associated with autoimmune conditions. Studies have identified these antibodies in diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and antiphospholipid syndrome, where they may contribute to altered lipid profiles and cardiovascular complications. By binding to LPL, these antibodies can inhibit its enzymatic function, impair triglyceride clearance, and exacerbate lipid abnormalities.
Research on LPL antibodies gained momentum due to their potential role in autoimmune-related hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis. Their presence is occasionally detected in patients with unexplained severe triglyceride elevation, suggesting an autoimmune etiology. Current investigations focus on understanding their pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic utility, and interplay with genetic or environmental factors affecting LPL expression.
While clinical significance remains under exploration, LPL antibodies represent a novel biomarker for autoimmune-associated dyslipidemia. Therapeutic strategies targeting these antibodies or restoring LPL activity, such as immunomodulatory therapies or gene-based interventions, are emerging areas of interest. Further studies are needed to clarify their prognostic value and therapeutic implications in metabolic and autoimmune disorders.
×