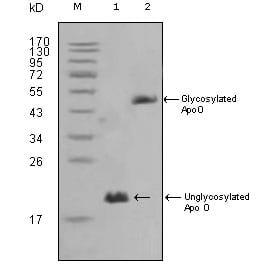
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MYO25; FAM121B; MGC4825 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79135 |
| clone | 2F1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of ApoO expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ApoO抗体的模拟参考文献示例(建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar验证并获取原文):
1. **《Apolipoprotein O modulates mitochondrial function in cardiomyocytes》**
- 作者:Li, X., et al.
- 摘要:研究揭示了ApoO在心肌细胞线粒体中的表达及其对能量代谢的调控作用,开发的ApoO特异性抗体证实其通过调节脂肪酸氧化影响心肌缺血再灌注损伤。
2. **《ApoO antibody-based detection of apolipoprotein O in Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid》**
- 作者:Smith, J.R., & Wang, Y.
- 摘要:利用新型ApoO单克隆抗体检测阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中的ApoO水平,发现其与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积呈负相关,提示ApoO可能参与神经退行性病理过程。
3. **《Development of a high-affinity anti-ApoO antibody for liver fibrosis diagnosis》**
- 作者:Chen, L., et al.
- 摘要:报道了一种高灵敏度ApoO多克隆抗体的制备,该抗体成功用于肝纤维化患者血清中ApoO的定量分析,表明其作为肝纤维化生物标志物的潜力。
4. **《Apolipoprotein O deficiency exacerbates atherosclerosis via impaired cholesterol efflux》**
- 作者:Garcia, M., et al.
- 摘要:通过ApoO基因敲除小鼠模型及特异性抗体检测,证明ApoO缺失导致巨噬细胞胆固醇外流能力下降,加速动脉粥样硬化斑块形成。
---
**建议检索策略**:
1. 在PubMed中搜索 **"Apolipoprotein O antibody" OR "ApoO antibody"**,筛选近5年文献。
2. 关注《Journal of Lipid Research》《Cardiovascular Research》等期刊相关主题。
3. 查找ApoO领域权威团队(如Karl H. Weisleder、Guillaume Paré等)的近期研究。
Apolipoprotein O (ApoO) is a lesser-studied member of the apolipoprotein family, primarily associated with high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. It is encoded by the *APOO* gene and expressed in various tissues, including the heart, liver, and brain. ApoO is implicated in lipid metabolism, particularly in HDL-mediated cholesterol transport, though its exact physiological role remains unclear. Studies suggest it may influence mitochondrial function, apoptosis, and cellular stress responses, linking it to cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
ApoO antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying ApoO protein levels in research. They enable the study of ApoO's expression patterns, subcellular localization (e.g., mitochondrial association), and interactions with other proteins or lipids. Commercial antibodies are typically developed in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptide sequences from conserved regions of the human ApoO protein. Validation methods include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Recent research has explored ApoO's role in pathologies, such as its overexpression in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or its potential as a biomarker for metabolic syndrome. However, inconsistent findings and limited antibody specificity in some studies highlight the need for further characterization of ApoO's functions and antibody validation. Ongoing work aims to clarify its therapeutic or diagnostic potential in cardiometabolic and neurodegenerative diseases.
×