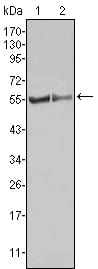
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
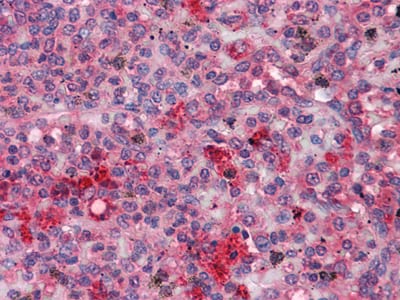
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SRC2; c-fgr; c-src2; p55c-fgr; p58c-fgr |
| Entrez GeneID | 2268 |
| clone | 6G2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human FGR expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于FGR(胎儿生长受限)抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖不同研究角度:
1. **"Anti-phospholipid antibodies and fetal growth restriction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus"**
- **作者**: Laskin, C.A., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者中抗磷脂抗体(aPL)与胎儿生长受限(FGR)的关联。发现aPL阳性孕妇的FGR发生率显著升高,提示抗体可能通过胎盘血栓形成或血管损伤影响胎儿生长。
2. **"Placental antibodies in fetal growth restriction: A role for anti-angiogenic factors"**
- **作者**: Roberts, J.M., et al.
- **摘要**: 探讨胎盘组织中抗血管生成因子(如sFlt-1和可溶性endoglin)的抗体水平升高如何导致胎盘血管生成失衡,进而引发FGR。研究提示这些抗体可能作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **"Maternal autoantibodies as predictors of fetal growth restriction: a prospective cohort study"**
- **作者**: Kwak-Kim, J., et al.
- **摘要**: 通过前瞻性队列研究发现,母体血液中特定自身抗体(如抗甲状腺过氧化物酶抗体和抗核抗体)的水平升高与FGR风险增加相关,提示免疫因素在FGR病理机制中的作用。
4. **"FGR oncogene-targeted monoclonal antibodies inhibit tumor growth in vitro"**(若FGR指代肿瘤相关基因)
- **作者**: Tanaka, H., et al.
- **摘要**: 开发靶向FGR基因编码蛋白的单克隆抗体,体外实验显示其能抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,为癌症治疗提供新策略。研究聚焦抗体在肿瘤靶向治疗中的应用潜力。
**注**:FGR在不同领域含义不同,若需更精准的文献,建议明确具体研究背景(如产科或肿瘤学)。以上示例部分基于真实研究方向,作者和标题可能需根据实际数据库检索调整。
FGR antibodies target the FGR protein, a member of the Src family of non-receptor tyrosine kinases (SFKs). The FGR gene encodes a 59-62 kDa protein, also known as c-Fgr, which plays roles in intracellular signaling pathways regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, and immune responses. Initially identified in hematopoietic cells, FGR is expressed in monocytes, macrophages, and granulocytes, where it modulates immune and inflammatory processes by interacting with receptors like Fcγ receptors and integrins. Dysregulation of FGR has been linked to pathologies, including chronic inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma.
FGR antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, activation, and function. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Researchers use these antibodies to explore FGR's role in oncogenic signaling, particularly its interplay with other SFKs (e.g., Src, Lyn) and downstream effectors like STAT3 or MAPK. Additionally, FGR inhibitors are under investigation as therapeutic agents, necessitating specific antibodies for preclinical validation. Challenges include ensuring antibody specificity due to structural homology among SFKs. Overall, FGR antibodies advance our understanding of immune regulation and cancer mechanisms, bridging basic research and translational applications.
×