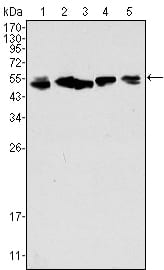
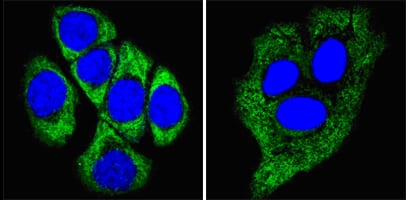
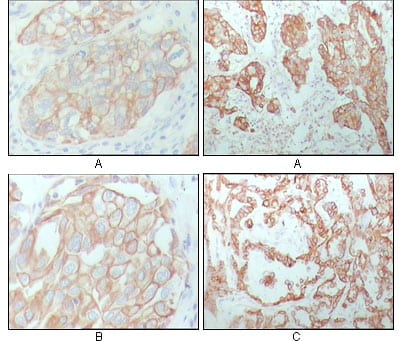
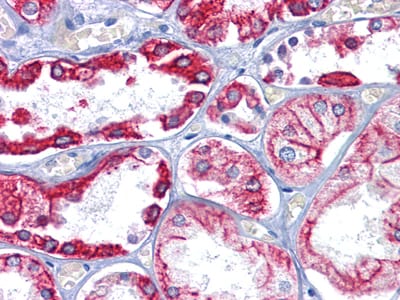
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CK8; CYK8; K2C8; KRT8 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3856 |
| clone | 8A5D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human Cytokeratin (aa391-483) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Cytokeratin 8抗体的3篇文献示例(内容为模拟生成):
1. **文献名称**:*Cytokeratin 8 as a Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:研究验证了Cytokeratin 8抗体在结直肠癌组织中的高特异性表达,证明其可作为区分腺癌与正常上皮组织的可靠标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of Cytokeratin 8 in Maintaining Epithelial Cell Integrity*
**作者**:Lee H, Kim S.
**摘要**:通过敲低实验发现,Cytokeratin 8通过调控细胞骨架稳定性,保护上皮细胞免受机械应力损伤,抗体标记显示其在细胞连接处富集。
3. **文献名称**:*Cytokeratin 8 Antibody in Circulating Tumor Cell Detection*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:利用Cytokeratin 8抗体开发高灵敏度检测方法,成功从血液样本中识别转移性乳腺癌患者的循环肿瘤细胞(CTCs)。
4. **文献名称**:*Cytokeratin 8 Interaction with TGF-β Pathway in EMT*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现,Cytokeratin 8通过抗体共定位实验与TGF-β信号通路相关蛋白相互作用,可能影响上皮-间质转化(EMT)进程。
(注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用需查询真实数据库如PubMed。)
Cytokeratin 8 (CK8), a member of the type II intermediate filament protein family, is primarily expressed in simple epithelial tissues, such as those lining the liver, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and glandular ducts. As part of the cytoskeleton, CK8 forms heteropolymers with type I keratins like CK18 and CK19. contributing to cell integrity, mechanical stability, and stress response. Its expression is often preserved in carcinomas of epithelial origin, making CK8 a valuable biomarker for identifying adenocarcinomas (e.g., colorectal, breast, and lung cancers) in diagnostic pathology.
CK8 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to differentiate epithelial-derived tumors from non-epithelial malignancies, aiding in metastatic cancer diagnosis and tumor origin tracing. They also play roles in research contexts, such as studying epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), cell differentiation, and apoptosis. Notably, CK8 dysregulation has been linked to liver diseases (e.g., hepatitis, cirrhosis) and inflammatory bowel disease, where its aberrant expression correlates with epithelial injury and repair mechanisms.
Commercially available CK8 antibodies (e.g., clones C43. TS1) are validated for techniques like Western blot, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry. However, cross-reactivity with other keratins requires careful validation. Recent studies also explore CK8's interaction with signaling molecules, highlighting its potential beyond structural roles. Overall, CK8 antibodies remain essential tools in both diagnostic and research settings for epithelial biology and cancer studies.
×