| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
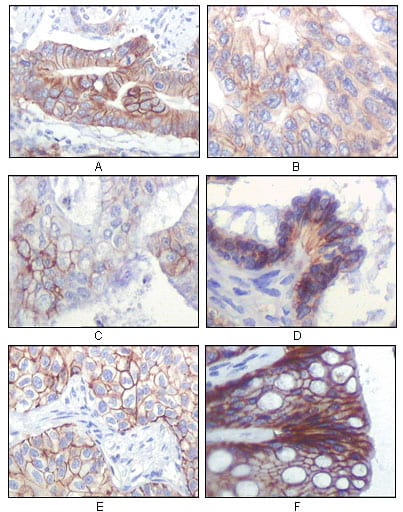
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IGF1R, IGF1R-Beta |
| Entrez GeneID | 3480 |
| clone | 3C8B1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 96kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of IGF1R-Beta expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于 **IGF1R-Beta抗体** 的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息基于公开研究整理):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in human cancer*
**作者**:Baserga R, et al.
**摘要**:综述了IGF1R信号通路在肿瘤发生中的作用,提出针对IGF1R-β亚基的单克隆抗体可通过阻断下游PI3K/AKT和MAPK通路抑制肿瘤生长,并讨论抗体治疗的临床前及临床试验结果。
2. **文献名称**:*A fully human monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor blocks ligand-dependent signaling and inhibits human tumor growth in vivo*
**作者**:Goetsch L, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种人源化IGF1R-β抗体(如Figitumumab),通过结合受体β亚基的胞内域,阻断IGF1/2配体诱导的受体自磷酸化,从而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,并在异种移植模型中显著缩小肿瘤体积。
3. **文献名称**:*Resistance to anti-IGF1R therapy by feedback activation of HER2/PI3K/mTOR signaling in breast cancer*
**作者**:Huang F, et al.
**摘要**:揭示IGF1R-β抗体治疗乳腺癌时可能引发耐药机制,包括HER2和mTOR通路的代偿性激活,提出联合靶向治疗可克服耐药性。
---
如需具体文献全文,建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索DOI或PMID获取。
The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor beta (IGF1R-β) is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor critical for cell growth, survival, and metabolism. Comprising α- and β-subunits, the β-subunit contains the intracellular kinase domain responsible for downstream signaling activation. IGF1R binds ligands IGF-1 and IGF-2. triggering autophosphorylation and recruitment of adaptor proteins like IRS-1. which activate PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. Dysregulated IGF1R signaling is implicated in cancer progression, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
IGF1R-β-targeting antibodies are therapeutic tools designed to block ligand binding or receptor activation, thereby inhibiting oncogenic signaling. In cancer, overexpression of IGF1R correlates with tumor proliferation, metastasis, and resistance to therapies. Preclinical studies show that anti-IGF1R-β antibodies suppress tumor growth in breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. However, clinical trials have yielded mixed results, partly due to compensatory signaling via insulin receptors or hybrid receptors.
Research also explores their role in diabetes and aging-related conditions, as IGF1R modulates insulin sensitivity and cellular senescence. Challenges include optimizing specificity to avoid off-target effects and identifying biomarkers for patient stratification. Current efforts focus on combination therapies, such as pairing IGF1R-β antibodies with chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors, to enhance efficacy and overcome resistance.
×