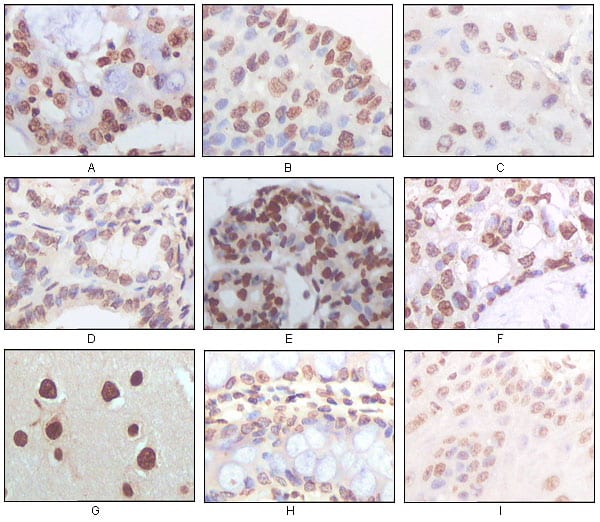
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Human P16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1029 |
| clone | 5A8A4; 3G8D12 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of P16 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与**Human p16抗体**相关的文献摘要信息,供参考:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types"*
**作者**:Kamb, A. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了**p16(CDKN2A)基因**在多种肿瘤中的失活突变,并通过特异性抗体检测p16蛋白表达缺失,验证了其作为肿瘤抑制因子的功能。研究为p16抗体在癌症诊断中的应用提供了理论基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"p16INK4a and p53 overexpression in the molecular diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia"*
**作者**:Sahebali, S. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用**p16抗体**(克隆E6H4)通过免疫组化技术检测宫颈病变组织中p16蛋白的过表达,证明其可作为高危HPV感染和癌前病变的生物标志物,显著提高诊断准确性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"Comparative analysis of p16 antibody clones for the detection of human papillomavirus-associated head and neck lesions"*
**作者**:Geradts, J. & Wilson, P.A.
**摘要**:研究系统比较了多种**p16抗体克隆**(如JC8、G175-405等)在头颈部肿瘤中的免疫反应性,发现不同克隆的敏感性和特异性差异,建议根据组织类型选择最优抗体。
---
如需具体文献链接或更多信息,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索标题或作者名获取全文。
The human p16 protein, encoded by the *CDKN2A* gene located on chromosome 9p21. is a critical tumor suppressor involved in cell cycle regulation. As a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI), p16 binds to CDK4/6. blocking their interaction with cyclin D and preventing phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein. This halts cell cycle progression at the G1/S checkpoint, allowing for DNA repair or apoptosis. Dysregulation of p16 is strongly associated with carcinogenesis; its inactivation via deletion, mutation, or promoter hypermethylation is observed in numerous cancers, including melanoma, pancreatic, and cervical cancers. Conversely, overexpression of p16 often correlates with cellular senescence or human papillomavirus (HPV)-related malignancies, where viral oncoproteins like E7 disrupt RB function, triggering p16 upregulation as a compensatory mechanism.
p16 antibodies are essential tools in research and diagnostics, widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect p16 expression in tissue samples. In clinical settings, p16 IHC serves as a surrogate marker for high-risk HPV infection in cervical and oropharyngeal cancers. These antibodies typically target epitopes in the conserved N-terminal region of the p16 protein, with clones like E6H4 being widely validated for diagnostic applications. Specificity and validation across sample types (e.g., formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues) are critical to ensure accurate interpretation. Beyond oncology, p16 antibodies are employed in aging studies, as p16 accumulation marks senescent cells. However, careful controls are required to distinguish pathological overexpression from physiological expression in benign or aging tissues.
×