| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
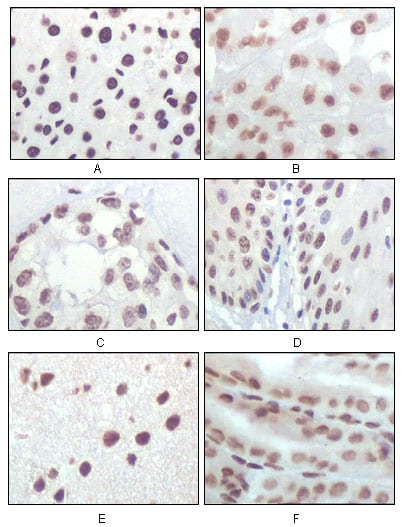
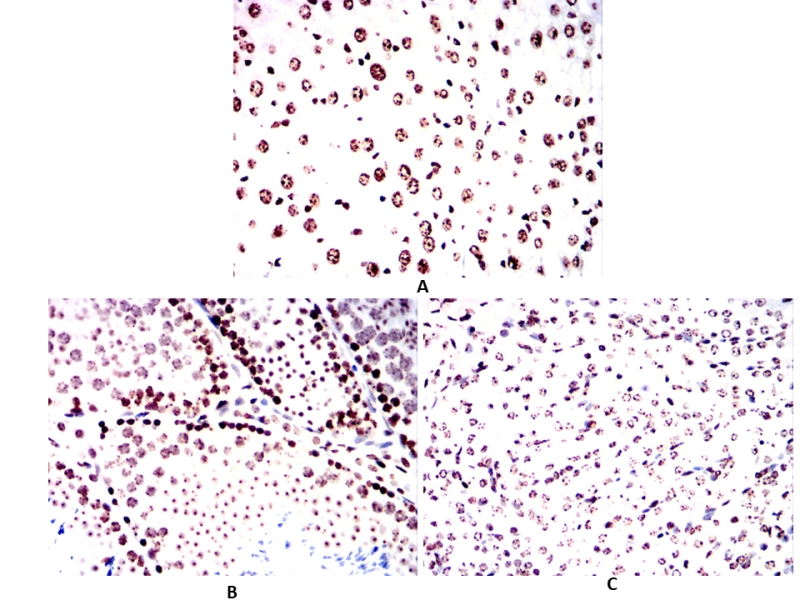
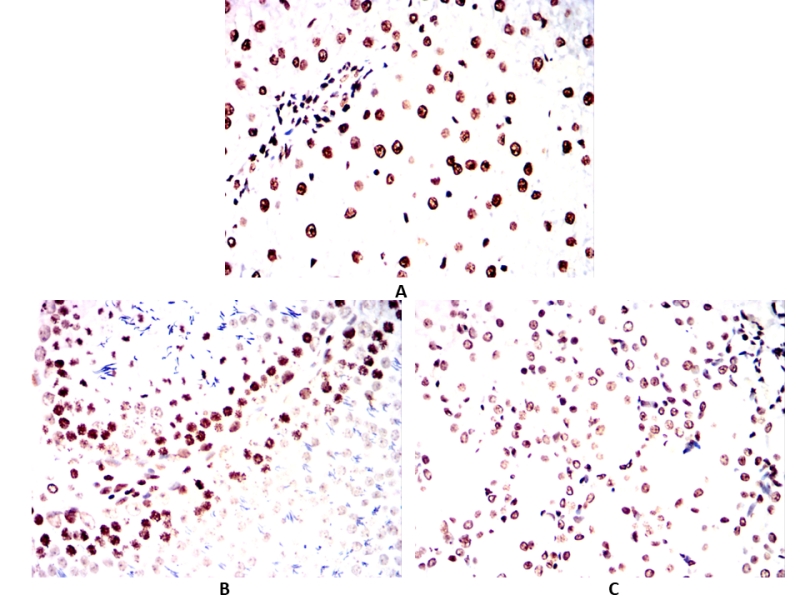
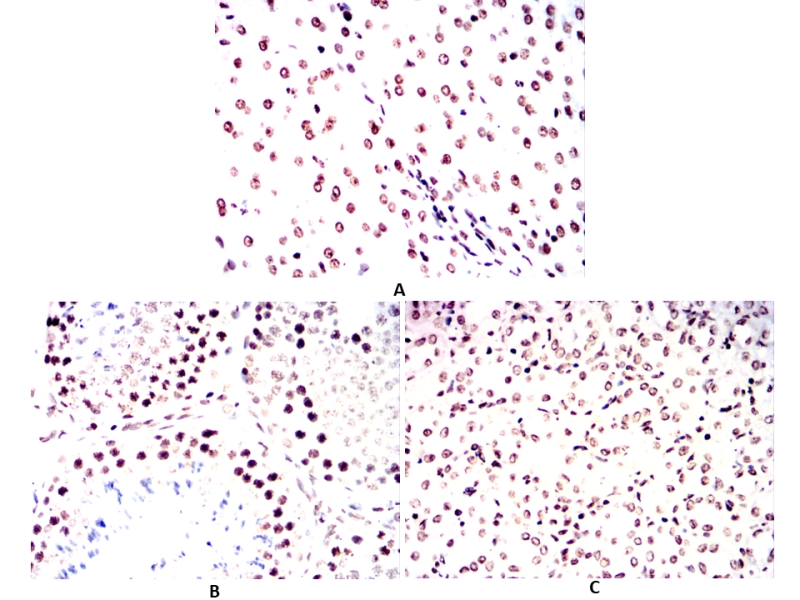
| IHC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Aliases | P16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1029 |
| clone | 1E12E10 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of P16 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于P16(人和小鼠)抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers*
**作者**:Nobori T, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过Western blot和免疫组化分析了多种人类肿瘤样本中P16蛋白的表达缺失,验证了P16抗体在检测肿瘤相关基因突变中的应用,揭示了P16在癌症发生中的抑癌作用。
2. **文献名称**:*p16INK4a induces an age-dependent decline in islet regenerative potential*
**作者**:Krishnamurthy J, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用小鼠模型和P16特异性抗体,通过免疫组化证明P16蛋白在衰老细胞中的积累,探讨了其在调控胰岛细胞再生能力中的作用,为衰老相关疾病研究提供了方法学参考。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of the INK4a locus in tumor suppression and cell mortality*
**作者**:Serrano M, et al.
**摘要**:该文献通过构建P16基因敲除小鼠,结合抗体检测(Western blot和免疫荧光),阐明了P16在细胞周期阻滞和肿瘤抑制中的关键功能,并验证了抗体在小鼠和人类细胞中的交叉反应性。
4. **文献名称**:*p16INK4a is a tumor suppressor in murine melanoma*
**作者**:Krimpenfort P, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用P16抗体在小鼠黑色素瘤模型中检测蛋白表达,证实P16缺失促进肿瘤进展,强调了该抗体在转基因动物模型分析中的特异性与可靠性。
这些文献涵盖了P16抗体在人类癌症样本分析、衰老研究及小鼠模型中的应用,涉及Western blot、免疫组化等实验方法。
The p16 protein, encoded by the CDKN2A gene, is a critical tumor suppressor that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4/6), thereby preventing G1-to-S phase progression. Dysregulation of p16 is implicated in various cancers, as its inactivation (via deletion, mutation, or promoter hypermethylation) disrupts cell cycle control, promoting uncontrolled proliferation. Additionally, p16 overexpression is associated with cellular senescence and aging.
Antibodies targeting p16 are essential tools in both research and diagnostics. Mouse- and human-specific p16 antibodies enable the detection of p16 expression across species, facilitating comparative studies in preclinical models (e.g., murine systems) and human tissues. These antibodies are widely used in techniques such as immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence to assess p16 status in tumors, senescent cells, or disease models. In clinical settings, p16 immunohistochemistry serves as a surrogate marker for high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection in cervical and head/neck cancers, aiding diagnosis and prognosis.
The development of cross-reactive antibodies (recognizing both mouse and human p16) enhances translational research, allowing consistent analysis of p16 pathways in vitro and in vivo. However, species-specific epitope variations necessitate rigorous validation to ensure specificity. Overall, p16 antibodies remain pivotal in elucidating oncogenic mechanisms, senescence biology, and therapeutic targeting of CDKN2A-related pathologies.
×