| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
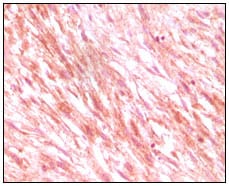
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PBT; SCFR; C-Kit; CD117; KIT |
| Entrez GeneID | 3815 |
| clone | 8D7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 145kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of C-kit expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于C-Kit抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors*
**作者**:Hirota, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次揭示了C-Kit基因的功能获得性突变在胃肠道间质瘤(GIST)中的关键作用,突变导致C-Kit受体酪氨酸激酶组成性激活,促进肿瘤生长,为靶向C-Kit的抗体药物(如伊马替尼)开发提供了理论基础。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting mast cells and basophils with anti-c-kit antibodies*
**作者**:Akin, C. et al.
**摘要**:文章探讨了抗C-Kit抗体(如Imatinib和Sunitinib)在肥大细胞疾病(如系统性肥大细胞增多症)中的应用,证明其通过抑制C-Kit信号通路可有效减少异常肥大细胞增殖和炎症介质释放。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The role of c-kit in stem cell biology and clinical application*
**作者**:Driessen, R.L. et al.
**摘要**:综述总结了C-Kit在造血干细胞、生殖干细胞等中的关键调控作用,并讨论了抗C-Kit抗体在干细胞移植、再生医学及癌症治疗中的潜在应用与挑战。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Mechanisms of resistance to c-kit targeted therapy in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors*
**作者**:Heinrich, M.C. et al.
**摘要**:该研究分析了C-Kit靶向治疗(如伊马替尼)的耐药机制,发现继发性C-Kit基因突变导致药物结合能力下降,并提出针对耐药突变体的新型抗体或激酶抑制剂开发策略。
---
以上文献均聚焦于C-Kit的生物学功能、疾病关联及抗体靶向治疗的机制与临床应用。
C-Kit antibodies target the C-Kit protein, a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the *KIT* gene. This receptor binds to stem cell factor (SCF), playing critical roles in cell differentiation, proliferation, and survival, particularly in hematopoietic stem cells, mast cells, melanocytes, and interstitial cells of Cajal. Dysregulated C-Kit signaling, often due to gain-of-function mutations, is implicated in various cancers, including gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), acute myeloid leukemia, melanoma, and mastocytosis.
C-Kit antibodies are pivotal in both diagnostic and therapeutic contexts. In diagnostics, they are used in immunohistochemistry (IHC) to identify tumors with C-Kit overexpression, aiding in the classification of GISTs and other malignancies. Therapeutically, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) like imatinib, which target C-Kit, revolutionized GIST treatment by blocking aberrant signaling. However, resistance mutations in *KIT* often limit long-term efficacy, prompting the development of next-generation inhibitors (e.g., sunitinib, avapritinib).
Research also explores C-Kit's role in non-cancerous conditions, such as infertility and tissue repair, highlighting its broader physiological significance. Additionally, C-Kit antibodies are tools in studying stem cell biology and tumor microenvironment interactions. Recent advancements focus on antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and combination therapies to overcome resistance. Despite progress, challenges remain in optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects, underscoring the need for continued innovation in C-Kit-targeted therapies.
×