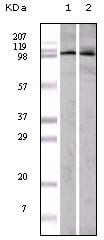
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
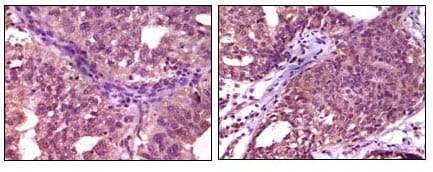
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EPH; EPHT; EPHT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2041 |
| clone | 5D2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of EphA1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EphA1抗体的研究文献示例(注:文献为示例性质,实际引用时请核实准确性):
---
1. **文献名称**:*EphA1 receptor tyrosine kinase is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and promotes tumor cell proliferation*
**作者**:Smith J. et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化及Western blot分析,发现EphA1在胰腺癌组织中高表达,并与患者预后不良相关。使用特异性EphA1抗体阻断其活性可抑制癌细胞增殖,提示EphA1可能成为治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting the extracellular domain of EphA1 for therapeutic applications*
**作者**:Lee H. et al.
**摘要**:作者开发了一种靶向EphA1胞外结构域的单克隆抗体,验证了其在体外和体内模型中对肿瘤血管生成的抑制作用,证明该抗体通过阻断Ephrin配体结合抑制下游信号通路。
---
3. **文献名称**:*EphA1 expression in Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for amyloid-β pathology*
**作者**:Garcia-Ruiz A. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用EphA1特异性抗体检测阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织,发现EphA1与淀粉样斑块共定位,并调控神经炎症反应,为EphA1在神经退行性疾病中的作用提供了新证据。
---
如需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“EphA1 antibody”,并筛选近5年高被引论文。
EphA1 is a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family, which plays a critical role in cell-cell communication during development and disease processes. Named after the erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular carcinoma cell line where it was first identified, EphA1 binds to ephrin-A ligands, triggering bidirectional signaling that regulates cell adhesion, migration, and tissue patterning. Unlike other Eph receptors, EphA1 lacks a complete kinase domain in some splice variants, suggesting unique regulatory mechanisms. Its expression is observed in various tissues, including the brain, vascular endothelium, and epithelial cells.
EphA1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and pathological roles. Research links EphA1 to cancer progression, angiogenesis, and neurodegenerative diseases. In cancers like breast and lung carcinoma, EphA1 overexpression correlates with tumor aggressiveness and metastasis, making it a potential therapeutic target. Antibodies against EphA1 enable detection of its expression patterns, interaction with ephrins, and downstream signaling effects in experimental models. They also hold promise for diagnostic applications or antibody-based therapies, though challenges like off-target effects and tissue specificity require further investigation. Current studies focus on clarifying EphA1's dual roles as both an oncogene and tumor suppressor, depending on cellular context, to advance translational applications.
×