| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
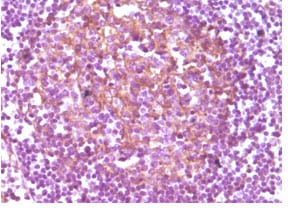
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
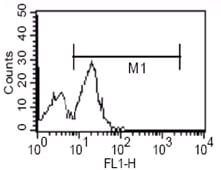
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD14 |
| Entrez GeneID | 929 |
| clone | 5A3 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD14 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD14抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD14. a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein*
**作者**:Wright, S. D. et al.
**摘要**:该研究发表于《Science》(1990年),首次阐明CD14作为脂多糖(LPS)及其结合蛋白复合物的受体功能。通过使用抗CD14单克隆抗体,研究者证明CD14在单核细胞中介导LPS诱导的炎症反应,为先天免疫机制提供了关键证据。
2. **文献名称**:*The CD14 antigen is a cell surface receptor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide*
**作者**:Goyert, S. M. et al.
**摘要**:发表于《Journal of Immunology》(1988年),作者利用抗CD14抗体成功克隆并鉴定了CD14分子,证实其在单核细胞表面结合LPS的功能,为后续开发CD14作为感染性疾病(如脓毒症)的诊断标志物奠定基础。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of CD14 in cellular recognition of bacterial lipopolysaccharides*
**作者**:Frey, E. A. et al.
**摘要**:该文(《Journal of Biological Chemistry》,2000年)通过抗CD14抗体的阻断实验,揭示了CD14与TLR4受体协同作用传递LPS信号的分子机制,强调了CD14在内毒素信号通路中的核心地位。
---
这些文献涵盖了CD14抗体在基础机制、诊断应用及信号通路研究中的关键作用。如需扩展,可补充特定疾病模型或临床研究的相关论文。
CD14 is a glycoprotein prominently expressed on the surface of monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, functioning as a co-receptor for bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in innate immune responses. It exists in two forms: membrane-bound (mCD14) anchored via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) tail and soluble (sCD14) circulating in plasma. CD14 facilitates LPS recognition by transferring it to the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/MD-2 complex, triggering pro-inflammatory cytokine production through NF-κB signaling. Antibodies targeting CD14 are essential tools in immunology research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development.
CD14 antibodies are categorized as monoclonal or polyclonal, with clones like 61D3 and MEM-18 widely used for flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to identify CD14⁺ immune cells or quantify soluble CD14 levels. In research, these antibodies help elucidate CD14's role in sepsis, atherosclerosis, and chronic inflammatory diseases. Clinically, CD14 antibodies have therapeutic potential; for example, blocking CD14 may attenuate LPS-induced inflammation in septic shock. However, most applications remain experimental, emphasizing their value in mechanistic studies rather than approved therapies.
The development of CD14 antibodies has advanced understanding of innate immunity and microbial pathogenesis, highlighting their dual role as research reagents and investigational therapeutic agents. Their specificity and versatility continue to support studies on immune cell differentiation, infection responses, and inflammatory disorders.
×