| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
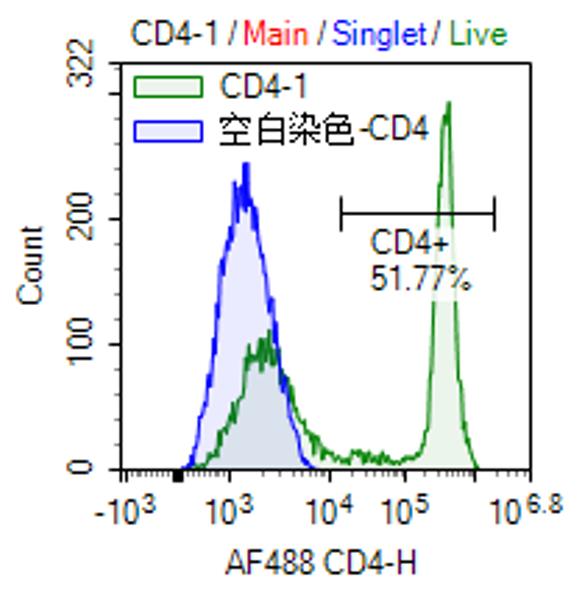
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD4mut |
| Entrez GeneID | 920 |
| clone | B486A1 |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD4 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3条关于CD4抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*CD4: A co-receptor in the immune response and HIV infection*
**作者**:Littman DR (1987)
**摘要**:该文献系统阐述了CD4分子作为T细胞受体(TCR)共受体在抗原识别中的作用,并揭示了HIV通过结合CD4感染宿主细胞的机制,为后续抗HIV抗体药物研发奠定理论基础。
2. **文献名称**:*Ibalizumab, a CD4-directed post-attachment HIV-1 inhibitor*
**作者**:Toma J et al. (2018)
**摘要**:报道了人源化单克隆抗体ibalizumab的III期临床试验结果,证明其通过靶向CD4分子第二结构域阻断HIV进入细胞,对多重耐药HIV患者具有显著疗效,成为首个获批的CD4导向治疗抗体。
3. **文献名称**:*CD4+ T cell depletion in HIV infection: mechanisms and therapeutic implications*
**作者**:Okoye AA, Picker LJ (2013)
**摘要**:分析了HIV感染中CD4+ T细胞耗竭的免疫学机制,探讨了基于CD4抗体调节免疫反应的潜在治疗策略,包括增强抗病毒免疫和减少免疫激活损伤的双重作用。
---
**备注**:以上文献为领域内代表性研究,涵盖基础机制(Littman, 1987)、药物开发(Toma et al., 2018)及病理机制与治疗探索(Okoye & Picker, 2013)。实际引用需核对具体期刊卷期信息。
CD4 antibodies target the CD4 glycoprotein, a key surface receptor predominantly expressed on helper T cells, regulatory T cells, and certain dendritic cells. The CD4 molecule plays a critical role in adaptive immunity by stabilizing interactions between T-cell receptors (TCRs) and MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells. It also facilitates signal transduction through its association with the tyrosine kinase Lck, promoting T-cell activation and differentiation.
CD4 antibodies are widely utilized in research and clinical applications. In basic science, they enable identification, isolation, and functional characterization of CD4+ T-cell subsets via flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. Therapeutic CD4 antibodies have been explored for modulating immune responses, particularly in autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis) and organ transplantation, where transient CD4+ T-cell depletion may suppress harmful immune activity. However, their use is complicated by risks of immunosuppression and incomplete efficacy.
Notably, CD4 serves as a primary receptor for HIV entry, making CD4 antibodies valuable in HIV research. Some antibodies block viral entry by binding to CD4. while others are used to study viral pathogenesis. Monoclonal antibodies like ibalizumab (targeting CD4) have been approved for multidrug-resistant HIV treatment. Despite their versatility, CD4 antibodies require precise targeting to avoid disrupting essential immune functions, underscoring the balance between therapeutic benefit and immunological safety.
×