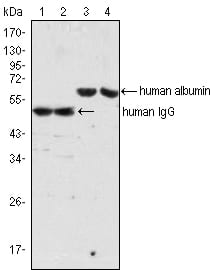
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| clone | 4D2D9G8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Human IgG was isolated from human sera and purified by chromatography. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于人类IgG抗体的参考文献及简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Structure and function of immunoglobulins*
**作者**:Schroeder, H. W., & Cavacini, L.
**摘要**:该综述详细解析了人类IgG抗体的结构(包括Fab和Fc区域),并讨论了其生物学功能,如中和病原体、激活补体系统及介导细胞毒性反应,强调了IgG亚型(IgG1-4)的功能差异。
2. **文献名称**:*Fcγ receptors as mediators of antibody effector activity*
**作者**:Nimmerjahn, F., & Ravetch, J. V.
**摘要**:研究聚焦于IgG抗体的Fc区域与Fcγ受体的相互作用,揭示了其在抗体依赖性细胞介导的细胞毒性(ADCC)和吞噬作用(ADCP)中的关键作用,为治疗性抗体设计提供理论依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic antibodies: successes, limitations and hopes for the future*
**作者**:Chames, P., et al.
**摘要**:总结了IgG类单克隆抗体在疾病治疗中的应用(如癌症、自身免疫病),探讨了工程化改造(如人源化、Fc优化)对药物疗效和安全性提升的贡献。
4. **文献名称**:*COVID-19 neutralizing antibodies: the path to clinical translation*
**作者**:Levine, A. G., et al.
**摘要**:以新冠病毒为例,分析了中和性IgG抗体的开发策略及临床效果,包括康复者血浆疗法和单克隆抗体药物的作用机制与挑战。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体引用请以实际论文或数据库为准。)
Human immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most abundant antibody class in the human circulatory system, constituting approximately 75% of serum antibodies. Produced by B cells, IgG plays a central role in adaptive immunity by recognizing and neutralizing pathogens, toxins, and foreign substances. Structurally, IgG is a Y-shaped glycoprotein composed of two identical heavy chains and two light chains, forming two antigen-binding fragments (Fab) and a crystallizable fragment (Fc). The Fab region binds to specific antigens, while the Fc region mediates effector functions such as complement activation and interaction with Fc receptors on immune cells.
Four IgG subclasses (IgG1-4) exist in humans, differing in heavy-chain structure, abundance, and functional properties. IgG1 is the most prevalent (60-65% of total IgG) and excels in pathogen neutralization, opsonization, and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). IgG2 primarily targets polysaccharide antigens, while IgG3 exhibits strong complement activation. IgG4. the least common, has anti-inflammatory properties and dynamic Fab-arm exchange capability.
IgG’s long serum half-life (~21 days) stems from pH-dependent FcRn receptor recycling, a feature exploited in therapeutic antibody design. As the primary antibody in secondary immune responses, IgG provides durable protection against reinfection. Its stability, specificity, and versatility make IgG a cornerstone of monoclonal antibody therapies for cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. However, subclass-specific variations in effector functions require careful selection in therapeutic applications to balance efficacy and safety.
×