关键信息
-
基因名
CD160
-
简介
CD160 is a diverse immune cell receptor that regulates activation and differentiation through stimulatory or inhibitory signaling. It exists in GPI-anchored and transmembrane form and initiates different pathways in NK and T cells. CD160 Protein, Mouse (HEK293, Fc) is the recombinant mouse-derived CD160 protein, expressed by HEK293 , with C-hFc labeled tag.
- 应用
-
别名
CD160 antigen; CD160
-
种属
Mouse
-
表达系统
HEK293
-
标签
C-hFc
-
纯度
Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
蛋白编号
O88875
-
表达区间
G28-L160
-
蛋白长度
Full Length of Mature Protein
-
分子量
55-65 kDa
-
内毒素
< 1.0 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method.
-
性状
Freeze-dried powder
-
缓冲液
PBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
-
复溶方法
Reconstitute in ddH2O to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
- 个性化定制
-
稳定性测试
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37℃ for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate isless than 8% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
-
保存条件 & 期限
Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20℃ to -80℃. Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
运输条件
In general, recombinant proteins are supplied as lyophilized powder and shipped at ambient temperature. For bulk packages, the proteins are provided as frozen liquid and shipped with blue ice, unless otherwise requested by the customer.
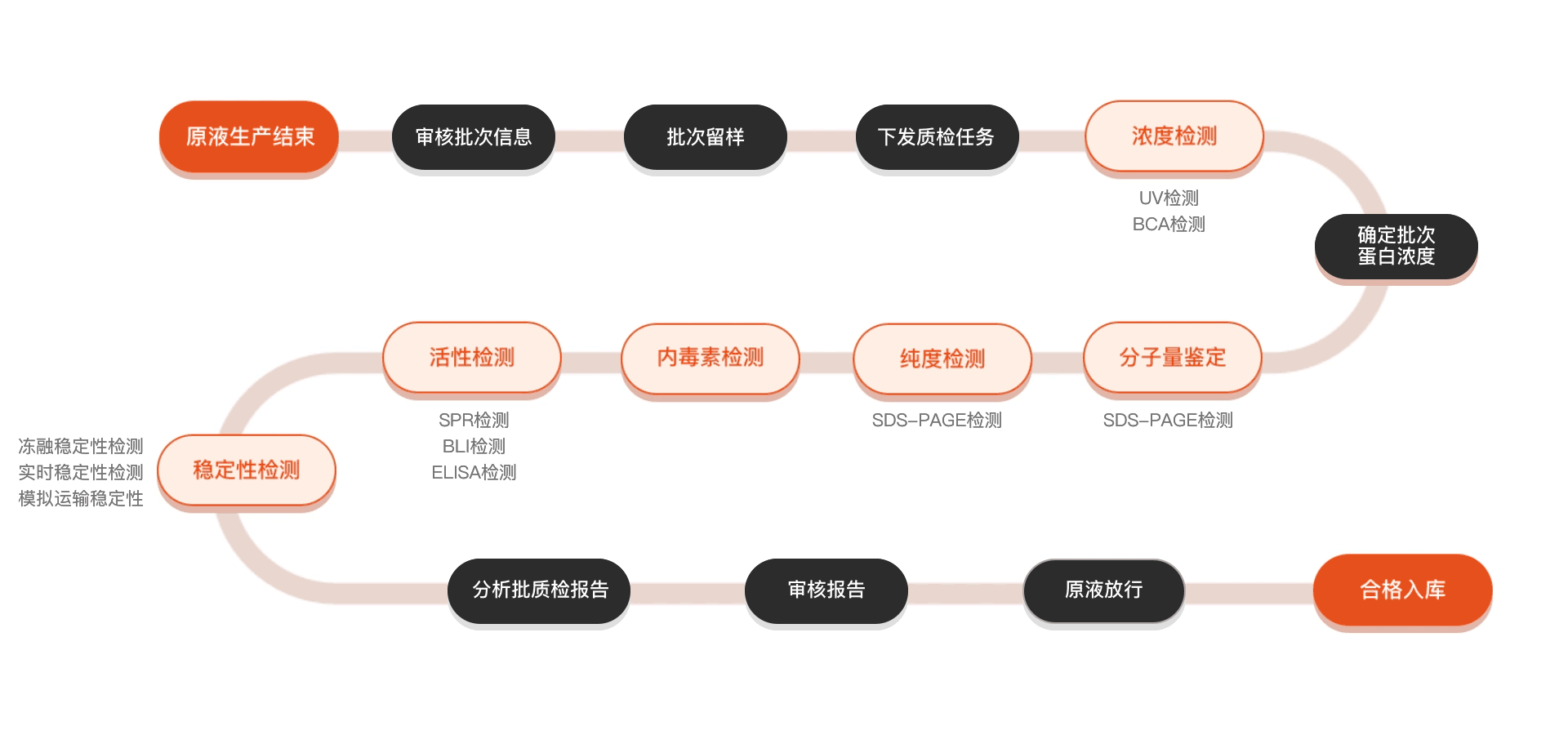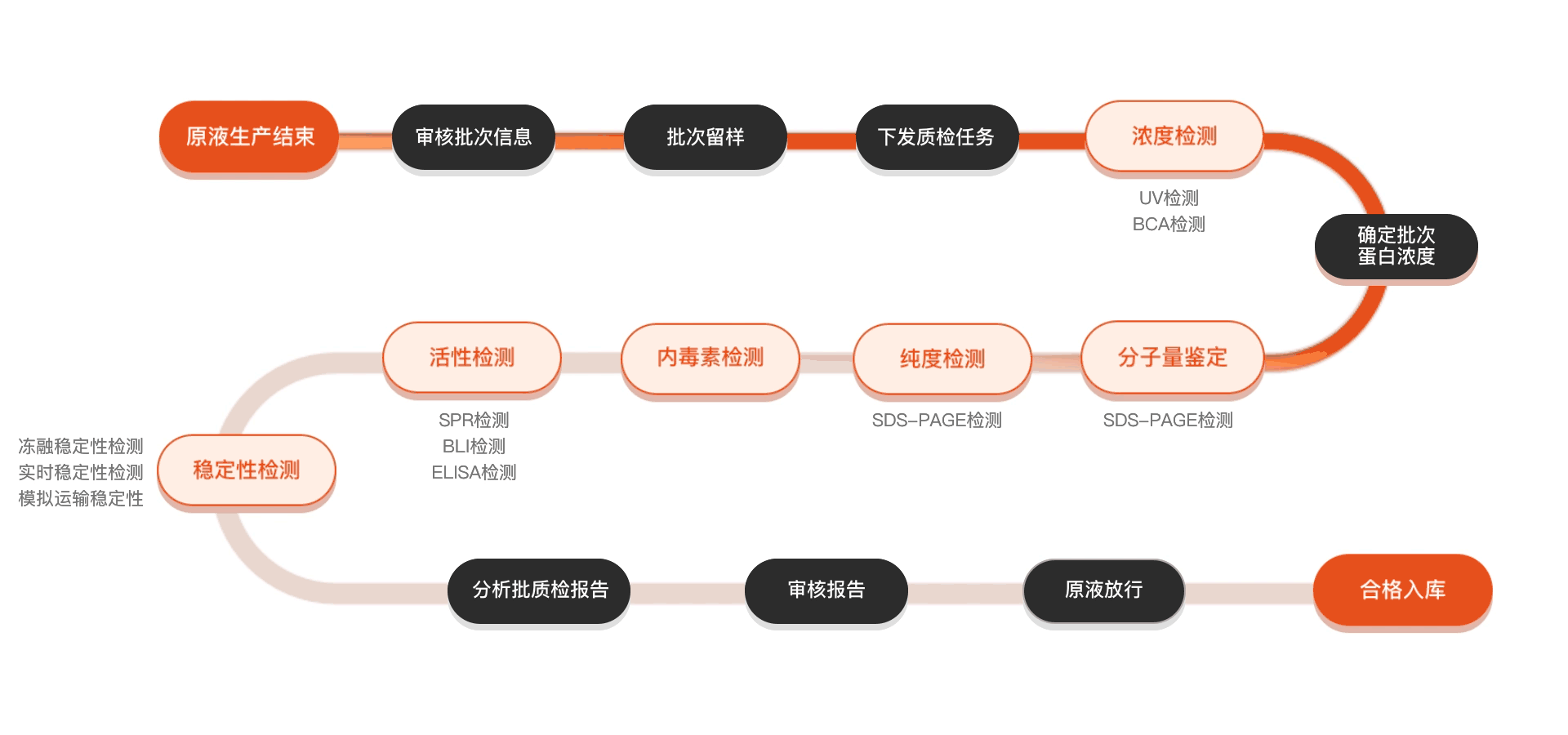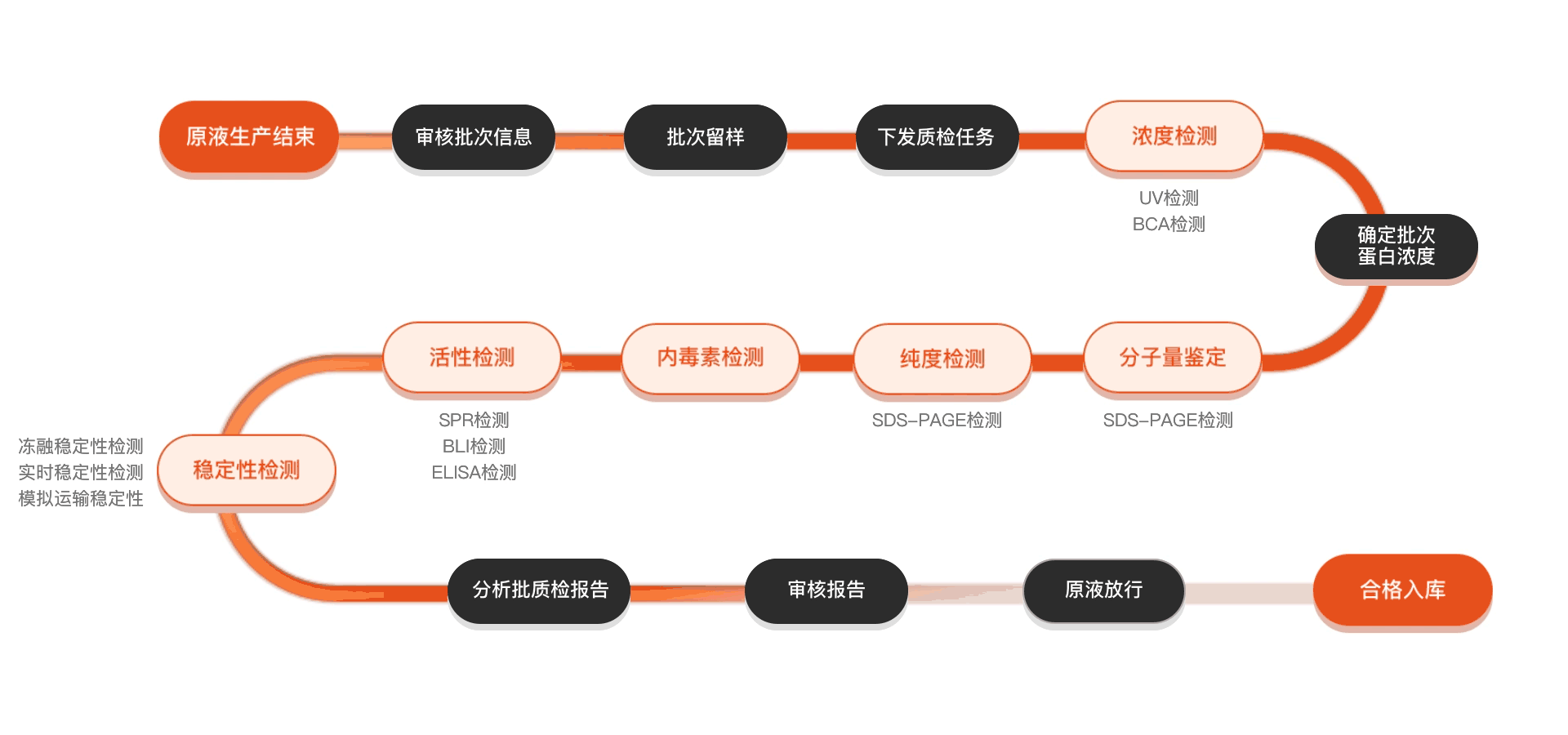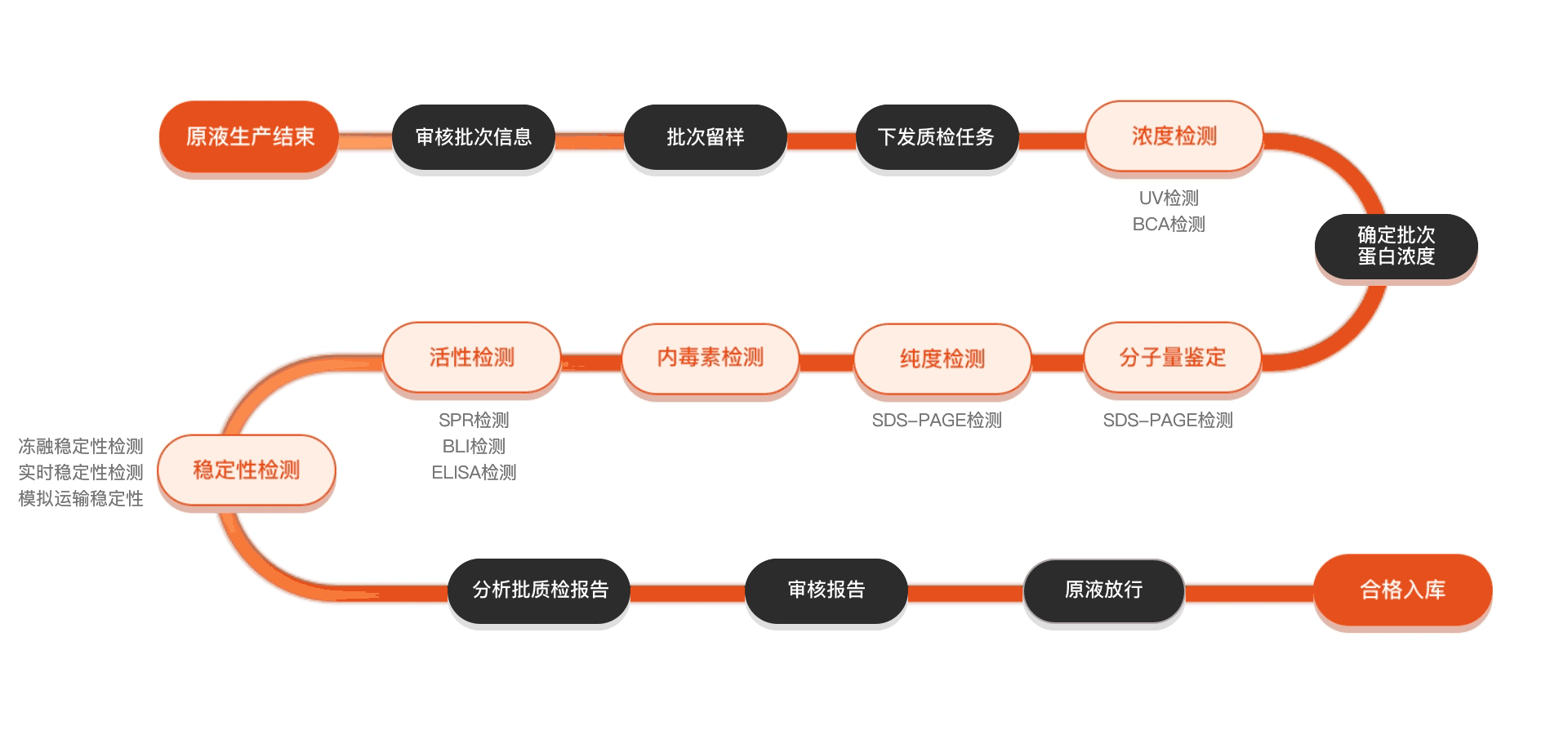
质检流程
相关产品
背景信息
CD160, also known as BY55, is an immune checkpoint receptor primarily expressed on the surface of certain immune cells such as natural killer (NK) cells and activated T cells. Its role in immunoregulation has garnered significant interest, particularly in the context of cancer immunotherapy. CD160 interacts with its ligands, which can inhibit immune responses, thus playing a critical role in maintaining immune homeostasis and potentially contributing to tumor immune evasion. Research has shown that CD160 can modulate the activation and cytotoxicity of NK cells, influencing tumor surveillance and the effectiveness of anti-tumor immunity. As a result, the development of CD160 recombinant proteins has emerged as a promising avenue for therapeutic interventions. Researchers are investigating how these proteins can be utilized to enhance immune responses against tumors, block inhibitory signals, and improve the efficacy of existing immunotherapies. The understanding of CD160's structure-function relationship, its signaling pathways, and ligand interactions is crucial for the design of novel targeted therapies. Additionally, CD160's potential as a biomarker for predicting clinical outcomes in cancer patients further emphasizes its importance in the field of immunology and oncology. Overall, the study of CD160 and its recombinant proteins holds significant promise for advancing cancer treatment strategies, potentially leading to more effective therapies that harness the body’s immune system to combat malignancies.