关键信息
-
基因名
Integrin beta-1/CD29
- 应用
-
别名
CD29; MSK12; ITG-B1; FNRB; GPIIA; MDF2; MSK12; VLAB; Fibronectin Receptor Beta Polypeptide; Antigen CD29 Includes MDF2; Glycoprotein IIa; VLA-4 subunit beta
-
种属
Human
-
表达系统
E. coli
-
标签
N- His & GST
-
纯度
Greater than 90% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE.
-
蛋白编号
P05556
-
表达区间
Gln467~Thr635
-
分子量
48kDa
-
内毒素
< 1.0 EU per μg protein as determined by the LAL method.
-
性状
Freeze-dried powder
-
缓冲液
PBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
-
复溶方法
Reconstitute in ddH2O to a concentration of 0.1-0.5 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
- 个性化定制
-
稳定性测试
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37℃ for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate isless than 8% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
-
保存条件 & 期限
Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20℃ to -80℃. Store it under sterile conditions at -20℃ to -80℃. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
运输条件
In general, recombinant proteins are supplied as lyophilized powder and shipped at ambient temperature. For bulk packages, the proteins are provided as frozen liquid and shipped with blue ice, unless otherwise requested by the customer.
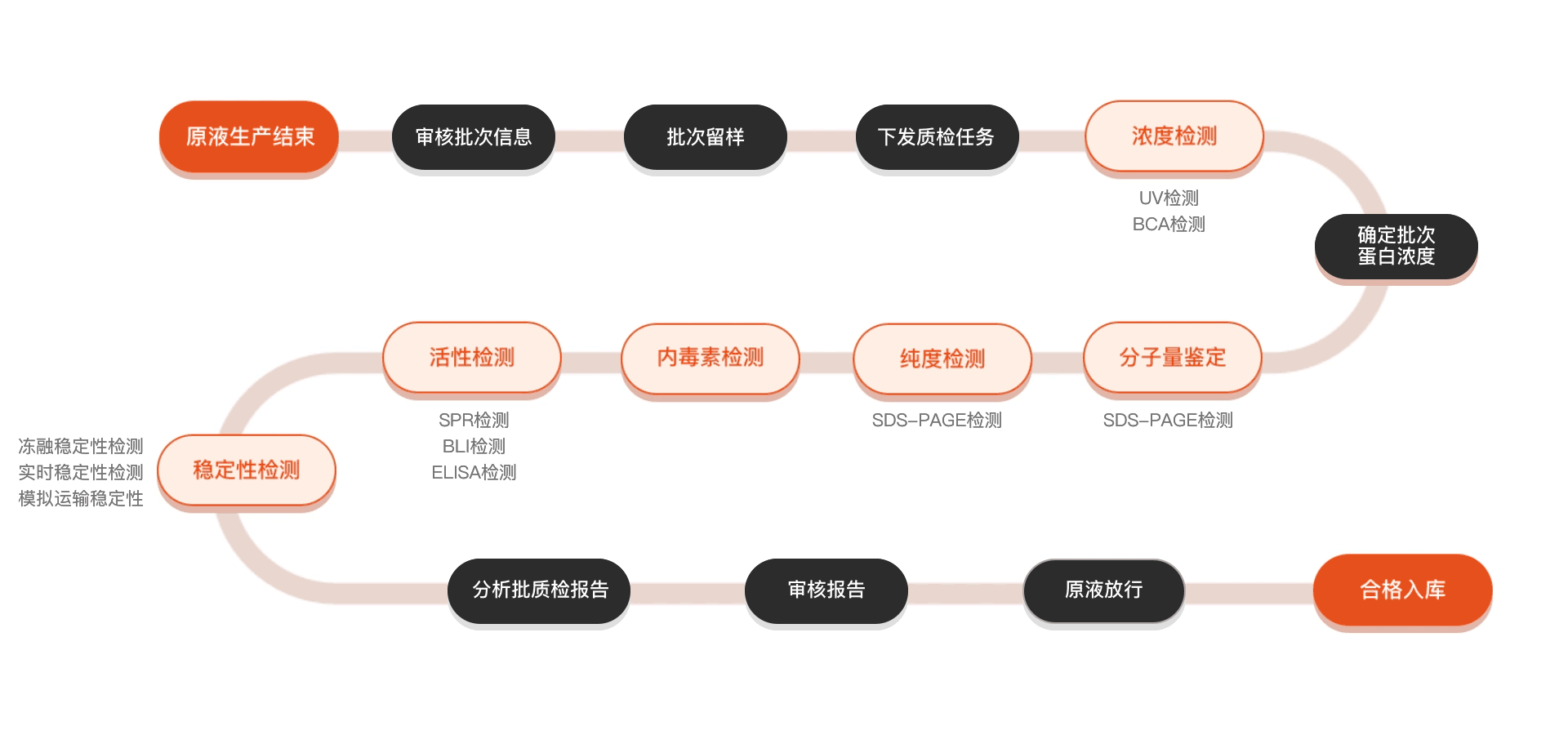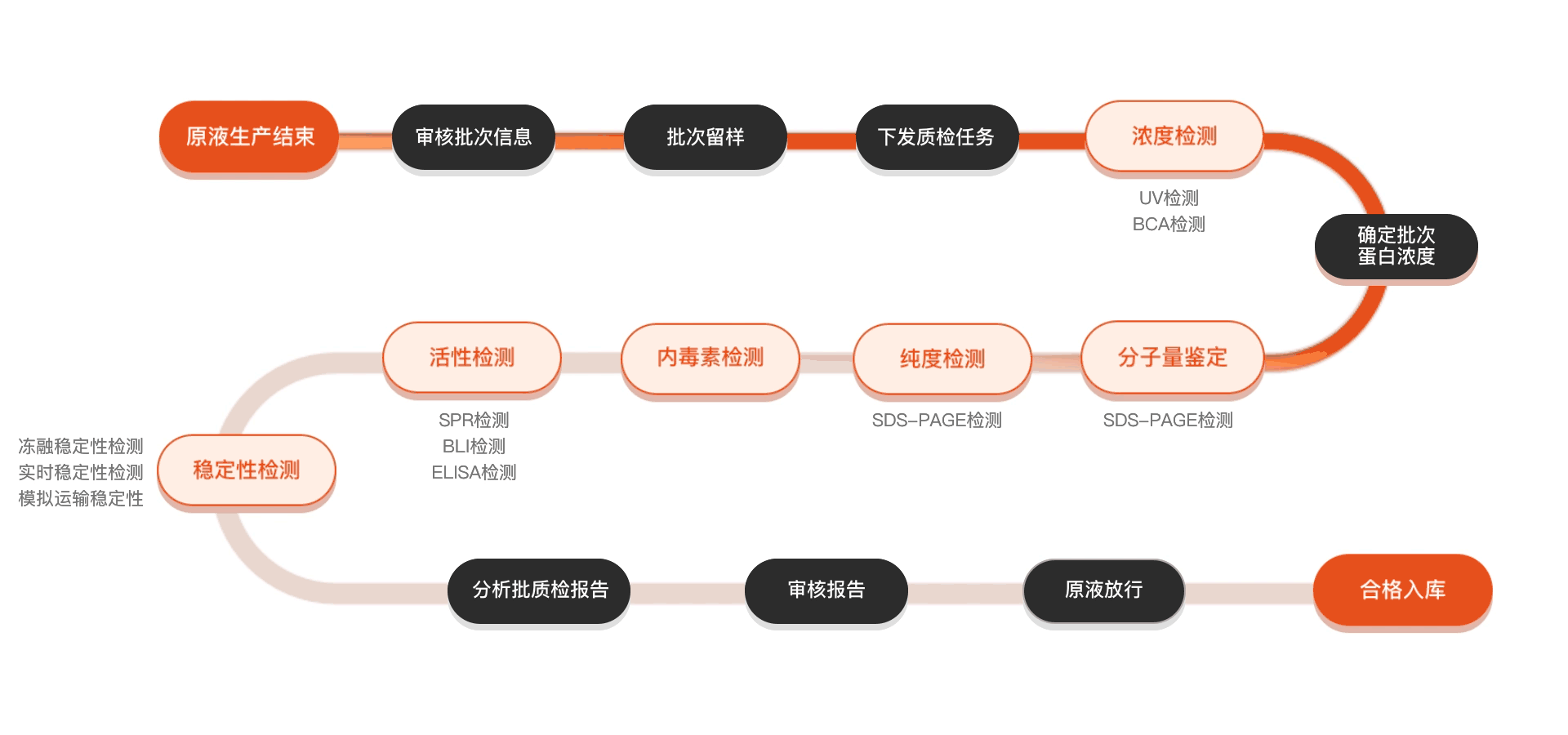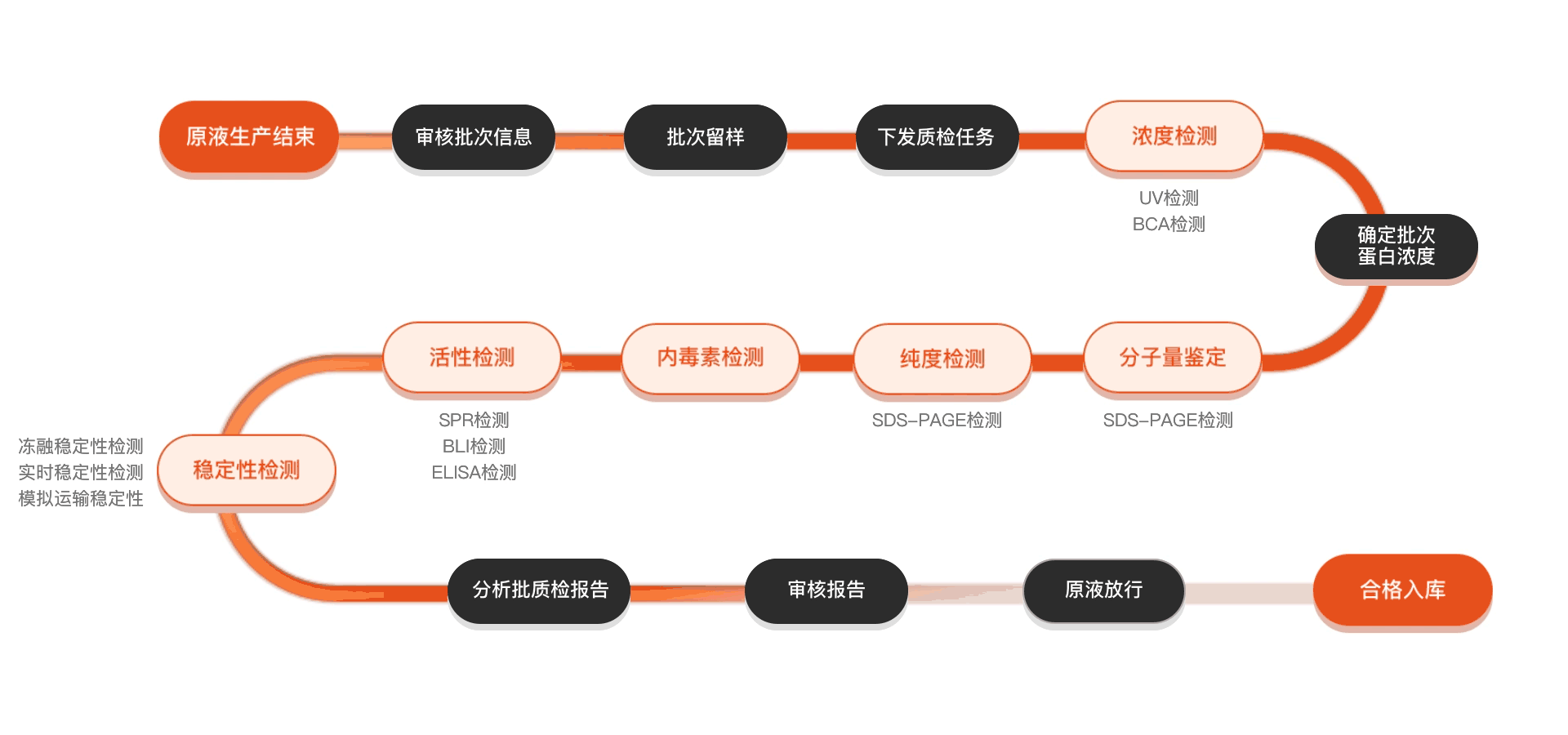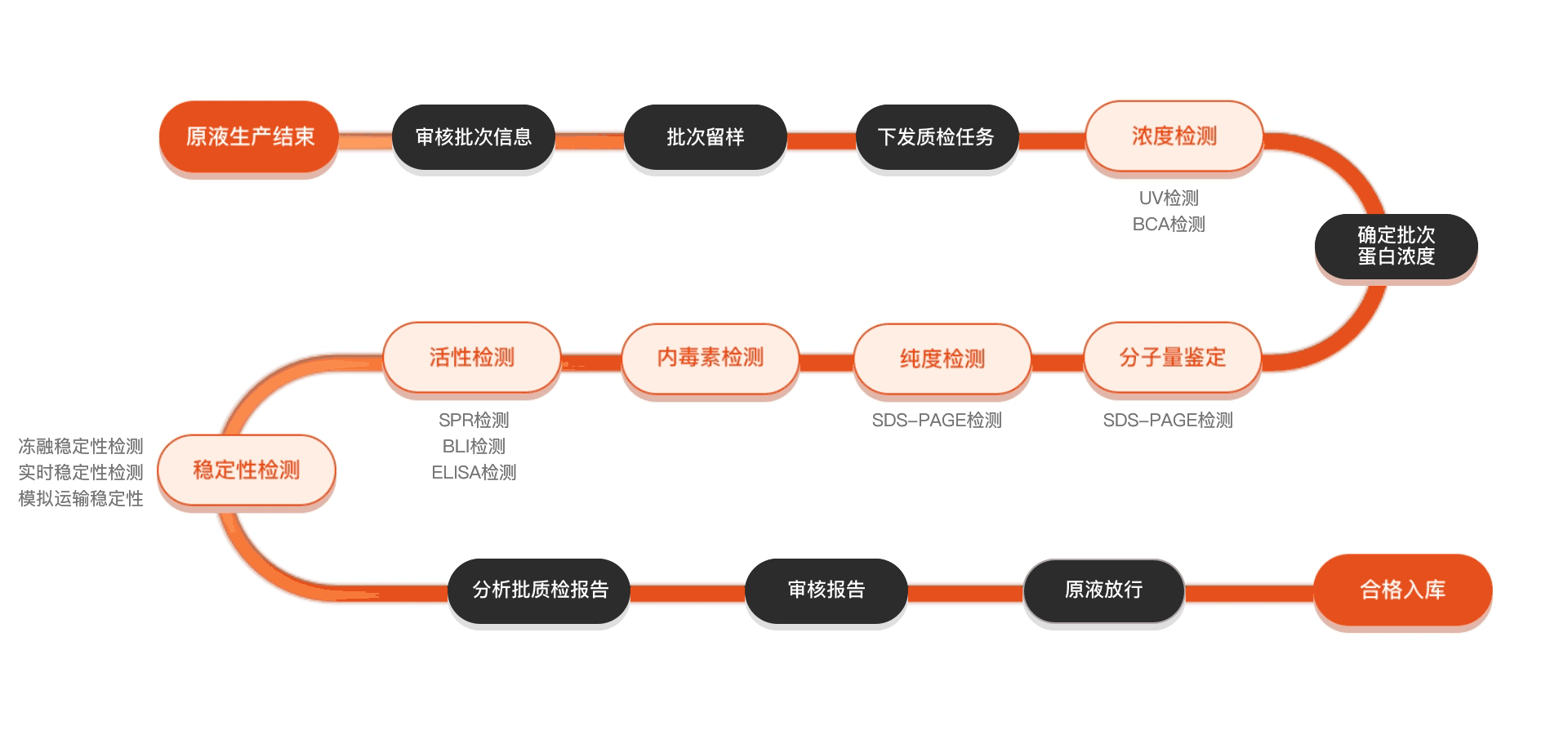
质检流程
相关产品
背景信息
Integrin beta-1, also known as CD29, is a crucial component of integrin receptors that mediate cell adhesion, migration, and signal transduction. Its involvement in various physiological and pathological processes, including embryogenesis, wound healing, and tumor progression, has garnered significant attention in biomedical research. The heterodimer formed by integrin beta-1 and its alpha partners facilitates interactions with the extracellular matrix (ECM) and other cell types, influencing cellular behavior and tissue organization. Research on recombinant integrin beta-1/CD29 proteins primarily aims to elucidate their structural and functional properties, as well as their roles in cell signaling pathways. These studies have significant implications for understanding diseases such as cancer, where altered integrin expression can affect tumor cell behavior and metastasis. Additionally, investigating recombinant forms of integrin beta-1 can aid in developing novel therapeutic strategies and biomaterials for regenerative medicine. Overall, the study of integrin beta-1/CD29 recombinant proteins is pivotal in advancing our knowledge of cell-matrix interactions and their implications in health and disease.