| WB | 1:200-1:1000 | human, mouse |
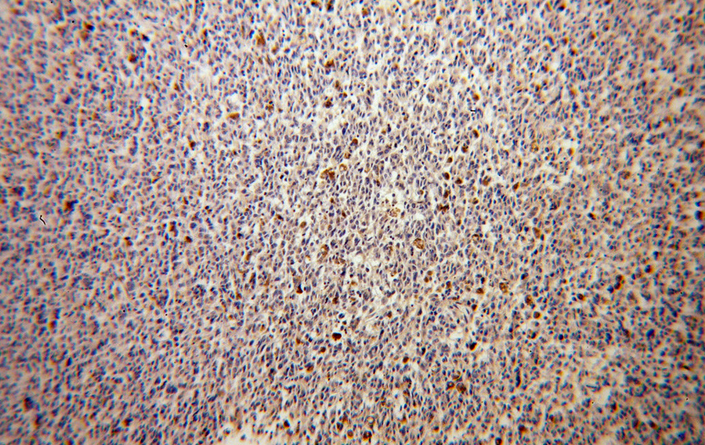
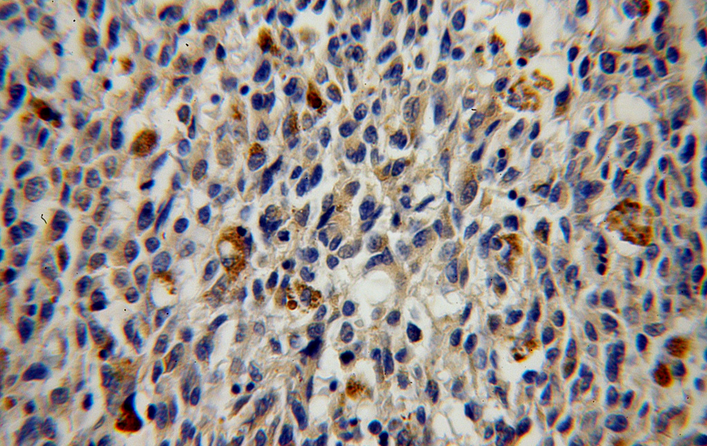
| IHC | 1:20-1:200 | human, mouse |
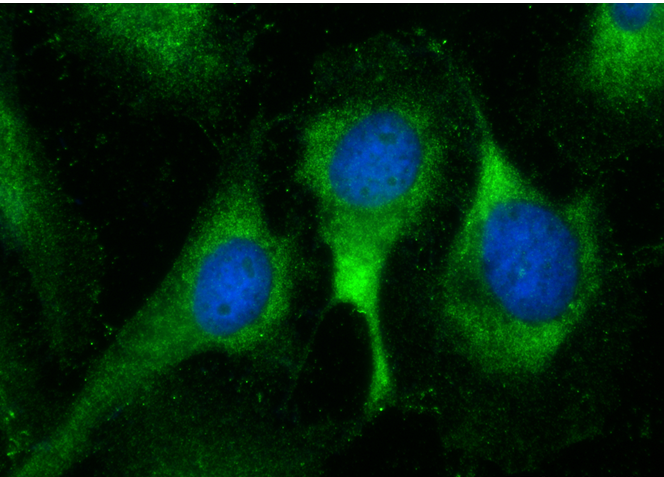
| IF/ICC | 1:200-1:800 | human, mouse |
| IP | 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate | human, mouse |
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IHC |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, rat |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | UDP-galactose-4-epimerase |
| 别名 | UDP-GlcNAc 4-epimerase, UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase, UDP-galactose 4-epimerase, SDR1E1, EC:5.1.3.7 |
| 计算分子量 | 38 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 38 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC050685 |
| 基因名称 | GALE |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2582 |
| RRID | AB_2108540 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14376 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
GALE (UDP-galactose-4-epimerase) is a crucial enzyme in the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, responsible for the interconversion of UDP-galactose and UDP-glucose. Antibodies targeting GALE have become important tools in biochemical and medical research due to the enzyme's central role in carbohydrate metabolism and its implications in galactosemia.
The development of GALE antibodies emerged from the need to study Type III galactosemia (GALE deficiency), a rare inherited metabolic disorder. Researchers first generated polyclonal antibodies against GALE in the 1990s using purified enzyme from microbial or mammalian sources. These early antibodies enabled the detection of GALE protein expression and its subcellular localization studies.
With advancements in hybridoma technology, monoclonal GALE antibodies were subsequently developed, offering higher specificity and reproducibility. These antibodies have been instrumental in:
Diagnosing GALE deficiency through Western blot analysis
Investigating tissue-specific expression patterns
Studying the enzyme's structural and functional properties
Developing therapeutic monitoring tools for potential treatments
Modern GALE antibodies are typically produced using recombinant GALE proteins as immunogens, with epitopes spanning various functional domains. They find applications in techniques including ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation. Recent studies have utilized these antibodies to explore GALE's potential roles beyond galactose metabolism, including its involvement in glycosylation processes and possible connections to cancer metabolism.
The commercial availability of GALE antibodies from multiple vendors has significantly accelerated research in metabolic disorders, with validation across human, mouse, and rat samples being particularly valuable for translational studies.
×