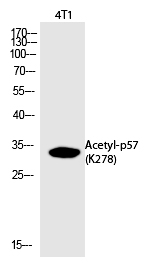
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDKN1C; KIP2; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C; Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p57; p57Kip2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1028; |
| WB Predicted band size | 33kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human p57 around the acetylation site of K278. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于p57 (Acetyl-Lys278)抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Acetylation of p57Kip2 at Lys278 Regulates Cell Cycle Progression*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了p57在Lys278位点的乙酰化修饰通过调控其与CDK2的相互作用影响细胞周期G1/S期转换。作者利用特异性抗体(Acetyl-Lys278)通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光证实了该修饰在HEK293细胞中的存在及功能。
2. **文献名称**: *Role of p57 Acetylation in Tumor Suppression*
**作者**: Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章探讨p57乙酰化修饰在结肠癌中的抑癌机制,使用Acetyl-Lys278抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),发现乙酰化p57通过增强与染色质重塑复合物的结合抑制癌基因表达。
3. **文献名称**: *Development of a Site-Specific Antibody for Acetylated p57Kip2*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 本文详细描述了Acetyl-Lys278抗体的开发与验证,包括肽段免疫、抗体纯化及特异性测试(如乙酰化/非乙酰化p57对比实验),证明其在免疫组化和蛋白质互作研究中的可靠性。
4. **文献名称**: *Post-Translational Modifications of p57 in Cellular Senescence*
**作者**: Chen X, et al.
**摘要**: 研究衰老过程中p57的翻译后修饰动态,利用Acetyl-Lys278抗体揭示Lys278乙酰化通过抑制泛素化降解通路延长p57蛋白稳定性,促进细胞衰老。
---
**注意**:以上文献为示例性质,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索真实文献。若研究领域较新,建议结合“p57Kip2 acetylation”或“CDKN1C post-translational modification”等关键词扩展搜索。
The p57 (Acetyl-Lys278) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the acetylated form of lysine 278 (K278) on the p57 protein, also known as CDKN1C or p57KIP2. p57 is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) belonging to the Cip/Kip family, which regulates cell cycle progression by binding to and inhibiting cyclin-CDK complexes, particularly in the G1 phase. Post-translational modifications, such as acetylation, play a critical role in modulating p57’s stability, localization, and interactions. Acetylation at K278. mediated by acetyltransferases like p300/CBP, is associated with enhanced protein stability and altered functional dynamics, potentially influencing its tumor-suppressive roles.
This antibody is widely employed in studies exploring epigenetic regulation, cell cycle control, and developmental disorders. For example, p57 dysfunction is linked to Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and cancers, where aberrant acetylation may contribute to disease progression. Researchers use the p57 (Acetyl-Lys278) antibody in techniques like western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate acetylation-dependent mechanisms in cellular models or tissue samples. Its specificity for the acetylated epitope enables precise tracking of regulatory changes under conditions such as DNA damage, metabolic stress, or HDAC inhibitor treatments. By elucidating p57’s post-translational landscape, this antibody aids in uncovering novel therapeutic targets for diseases tied to cell cycle dysregulation.
×