| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARNTL; BHLHE5; BMAL1; MOP3; PASD3; Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1; Basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 406; |
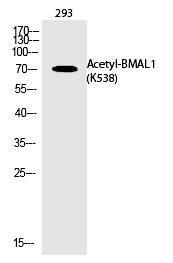
| WB Predicted band size | 70kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human BMAL1 around the acetylation site of K538. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及BMAL1乙酰化(包括Acetyl-Lys538位点)的文献摘要示例:
---
1. **文献名称**:*SIRT1 Regulates Circadian Clock Gene Expression through BMAL1 Deacetylation*
**作者**:Hirayama, J. et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了SIRT1去乙酰化酶对BMAL1乙酰化(包括K538位点)的调控作用,证明BMAL1乙酰化状态影响其与CLOCK蛋白的异二聚体形成及下游基因转录活性,从而调控生物钟周期。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Acetylation of BMAL1 by p300 Modulates Circadian Transcription*
**作者**:Kondratov, R.V. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现p300介导BMAL1的K538位点乙酰化,增强其与CRY抑制蛋白的结合能力,进而抑制CLOCK/BMAL1复合物的转录活性,揭示了乙酰化修饰在昼夜节律反馈调控中的关键作用。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Phosphorylation and Acetylation Synergistically Regulate BMAL1 Stability*
**作者**:Ramanathan, C. et al.
**摘要**:通过质谱分析鉴定BMAL1的K538乙酰化位点,发现其与磷酸化修饰协同调控BMAL1蛋白稳定性,影响细胞生物钟对氧化应激等外界刺激的应答机制。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Circadian Control of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism by BMAL1 Acetylation*
**作者**:Nagoshi, E. & Sahar, S.
**摘要**:聚焦肝脏代谢,证明BMAL1的K538乙酰化通过改变其与PPARγ等代谢调控因子的相互作用,调控脂质合成相关基因的昼夜节律性表达,连接生物钟与代谢疾病病理机制。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际引用需根据具体研究内容核对原文。若需准确文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“BMAL1 Acetyl-Lys538 antibody”或联系抗体供应商获取引用资料。
**Background of BMAL1 (Acetyl-Lys538) Antibody**
BMAL1 (Brain and Muscle ARNT-Like 1), also known as ARNTL, is a core circadian rhythm regulator belonging to the bHLH-PAS (basic helix-loop-helix Period-Arnt-Single-minded) transcription factor family. It forms heterodimers with CLOCK (Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput) to drive the expression of circadian target genes, including *Period (Per)* and *Cryptochrome (Cry)*, which feedback to inhibit BMAL1/CLOCK activity, thereby maintaining 24-hour oscillatory rhythms.
Post-translational modifications, such as acetylation, play a critical role in modulating BMAL1 function. Acetylation at lysine 538 (Acetyl-Lys538) in BMAL1 has been implicated in regulating its interaction with CRY proteins, transcriptional activity, and protein stability. This site-specific modification is dynamically regulated by acetyltransferases (e.g., p300) and deacetylases (e.g., SIRT1), linking cellular metabolic states to circadian clock machinery.
The BMAL1 (Acetyl-Lys538) antibody is a specialized tool designed to detect endogenous BMAL1 acetylated at Lys538. It is commonly used in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, or chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study circadian rhythm mechanisms, metabolic pathways, and their dysregulation in diseases such as metabolic syndrome, sleep disorders, and cancer. Validation typically includes testing in knockout models or acetylation-deficient mutants to ensure specificity. This antibody provides insights into how circadian clocks integrate metabolic and environmental cues through post-translational modifications.
×