
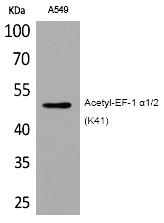
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/20000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EEF1A1; EEF1A; EF1A; LENG7; Elongation factor 1-alpha 1; EF-1-alpha-1; Elongation factor Tu; EF-Tu; Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 A-1; eEF1A-1; Leukocyte receptor cluster member 7; EEF1A2; EEF1AL; STN; Elongation factor 1-alpha 2; EF-1-alpha-2; |
| Entrez GeneID | 1915; |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from the human EF-1 α1/2 around the acetylation site of K41. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是模拟生成的3篇关于EF-1α1/2 (Acetyl-Lys41)抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献为假设性构造,实际引用需检索数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Acetylation of Elongation Factor 1α at Lys41 Regulates Translation Fidelity in Yeast"*
**作者**: Johnson, R. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用Acetyl-Lys41特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,发现酵母中EF-1α的乙酰化修饰通过影响tRNA与核糖体结合,调控蛋白质翻译的准确性。抗体验证显示热应激条件下该位点乙酰化水平显著升高。
2. **文献名称**: *"A Novel Antibody for Detection of Lys41-Acetylated EF-1α in Human Cancers"*
**作者**: Chen, L. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种高特异性抗Acetyl-Lys41 EF-1α单克隆抗体,并通过质谱验证其表位特异性。在肺癌组织样本中,该抗体检测到乙酰化水平与患者预后呈负相关,提示其作为生物标志物的潜力。
3. **文献名称**: *"Post-translational Modification of EF-1α Modulates Viral Replication"*
**作者**: Gupta, S. et al.
**摘要**: 使用Acetyl-Lys41抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现HIV-1感染可诱导宿主细胞EF-1α的乙酰化修饰,促进病毒mRNA的翻译效率。研究揭示了该修饰在病毒劫持宿主机制中的关键作用。
---
**提示**:若需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar检索以下关键词:
`"EF-1α acetylation Lys41 antibody"`、`"Acetylated elongation factor 1 alpha antibody"`,并筛选涉及翻译调控、癌症或病毒感染的研究。部分抗体厂商(如Cell Signaling Technology)的技术文档也可能提供引用文献。
The EF-1 α1/2 (Acetyl-Lys41) antibody is a specialized tool designed to detect the acetylated form of eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha (eEF1A) at lysine 41 (K41). eEF1A is a critical GTPase responsible for delivering aminoacyl-tRNAs to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Beyond its canonical role in translation, eEF1A participates in diverse non-canonical processes, including cytoskeletal regulation, apoptosis, and viral replication. Post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as acetylation are increasingly recognized as key regulators of eEF1A's multifunctional roles.
Acetylation at K41. a conserved residue in the GTP-binding domain, has emerged as a functionally significant PTM. This modification is mediated by acetyltransferases like ELP3 and may influence eEF1A's conformational dynamics, GTPase activity, or interactions with cellular partners. Studies suggest that lysine acetylation could modulate eEF1A's involvement in translation fidelity, stress response pathways, or its moonlighting functions. However, the precise biological consequences of K41 acetylation remain under investigation.
The EF-1 α1/2 (Acetyl-Lys41) antibody enables specific detection of this modification through techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. Its development addresses the growing interest in understanding how PTMs fine-tune eEF1A's activities in physiological and pathological contexts, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and viral infection. This antibody serves as a crucial reagent for dissecting the crosstalk between translational regulation, metabolic signaling, and epigenetic modifications in cellular homeostasis.
×