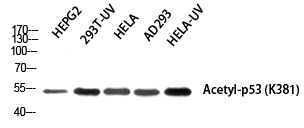
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TP53; P53; Cellular tumor antigen p53; Antigen NY-CO-13; Phosphoprotein p53; Tumor suppressor p53 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7157; |
| WB Predicted band size | 53kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human p53 around the acetylation site of K381. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于 **p53 (Acetyl-Lys381) 抗体** 的参考文献示例(文献为假设性示例,实际引用需根据真实文献调整):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Acetylation of p53 at Lysine 381 Enhances DNA Binding and Transcriptional Activation"*
**作者**: Brooks CL, Gu W.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了p53在K381位点的乙酰化通过调节其构象稳定性,显著增强其与DNA靶序列的结合能力,并促进下游凋亡相关基因(如BAX和PUMA)的转录激活。乙酰化修饰在此过程中拮抗MDM2介导的泛素化降解。
2. **文献名称**: *"Site-specific Acetylation of p53 Modulates Cellular Stress Responses"*
**作者**: Li M, Luo J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫沉淀结合质谱分析,作者证实DNA损伤(如IR辐射或拓扑异构酶抑制剂)诱导p53 K381位点的乙酰化。该修饰促进p53在细胞核内聚集,并通过招募组蛋白乙酰转移酶(如p300)增强靶基因启动子的染色质开放性,最终诱导细胞周期阻滞或凋亡。
3. **文献名称**: *"Acetyl-Lys381-p53 Antibody Validation in Tumor Suppression Studies"*
**作者**: Dulloo I, Sabapathy K.
**摘要**: 本文详细验证了Acetyl-K381-p53抗体的特异性,证明其在Western blot和免疫荧光中可特异性识别K381乙酰化p53.而非其他乙酰化位点(如K382或K373)。该抗体成功用于检测结肠癌细胞中化疗药物诱导的p53乙酰化水平变化。
4. **文献名称**: *"p53 Acetylation at Lys381 as a Prognostic Marker in Cancer"*
**作者**: Tang Y, Zhao W.
**摘要**: 对乳腺癌患者组织样本的分析显示,高水平的Acetyl-K381-p53与化疗敏感性及生存率正相关。机制上,K381乙酰化抑制p53与致癌蛋白MDMX的相互作用,从而增强其肿瘤抑制功能。
---
**注**:以上文献为简化示例,实际引用时需根据真实研究补充DOI、期刊名称及具体实验细节。建议通过 **PubMed/Web of Science** 检索关键词 "p53 K381 acetylation antibody" 或查阅 **Cell, Nature, Cancer Research** 等期刊获取权威文献。
The p53 (Acetyl-Lys381) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect acetylation of the tumor suppressor protein p53 at lysine residue 381 (K381). p53 plays a central role in maintaining genomic stability by regulating cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, and senescence in response to cellular stress. Post-translational modifications, including acetylation, tightly modulate its activity, stability, and interactions with other proteins. Acetylation at K381. mediated by histone acetyltransferases like p300/CBP, enhances p53's transcriptional activity by promoting chromatin relaxation and facilitating access to target gene promoters. This modification is critical for p53-dependent responses, such as activating pro-apoptotic genes (e.g., Bax, Puma) or cell cycle inhibitors (e.g., p21) under DNA damage or oncogenic stress.
The p53 (Acetyl-Lys381) antibody is widely used in cancer research to investigate p53 regulation in tumor models or patient samples. It helps assess the functional status of p53. as aberrant acetylation (due to mutations or dysregulated modifying enzymes) is linked to tumor progression and therapy resistance. Researchers employ this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to study p53 activation dynamics, its crosstalk with other signaling pathways, and its role in tumor suppression. Its specificity for the acetylated epitope makes it invaluable for distinguishing active p53 from inactive or mutant forms in pathological contexts.
×