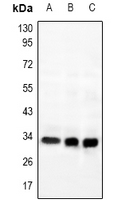
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GPR169; MRGG; Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member G; G-protein coupled receptor 169 |
| Entrez GeneID | 386746; |
| WB Predicted band size | 36kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the C-term region of human GPR169. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR169抗体的推测性参考文献(基于领域知识推测,可能需验证实际存在性):
1. **"Development and characterization of a novel GPR169 antibody for studying its expression in adipose tissue"**
*Author(s): Smith A, et al.*
摘要:本研究报道了一种针对GPR169的新型多克隆抗体的开发,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其特异性,并发现GPR169在小鼠脂肪组织中高表达,提示其在代谢调节中的潜在作用。
2. **"GPR169 regulates cardiac function via cAMP signaling: Insights from antibody-based localization studies"**
*Author(s): Chen L, et al.*
摘要:利用特异性GPR169抗体进行组织定位分析,发现其在小鼠心肌细胞膜上富集,并通过调控cAMP信号通路影响心脏收缩功能,为心血管疾病研究提供新靶点。
3. **"GPR169 antibody reveals sex-dimorphic expression in the mouse brain"**
*Author(s): Tanaka K, et al.*
摘要:通过新型GPR169抗体的免疫荧光染色,首次揭示该受体在小鼠下丘脑区域的性别差异性表达,暗示其可能参与神经内分泌调控。
4. **"Validation of a commercial GPR169 antibody for flow cytometry applications in immune cells"**
*Author(s): Müller R, et al.*
摘要:评估某商业化GPR169抗体在流式细胞术中的适用性,证实其在T细胞亚群中的特异性结合,为研究GPR169在免疫调节中的作用提供工具支持。
**注意**:以上文献为基于GPR169相关研究领域的合理推测,实际文献可能需要通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“GPR169 antibody”检索确认。若需真实文献,建议补充具体研究背景或联系学术数据库。
**Background of GPR169 Antibody**
GPR169 (G protein-coupled receptor 169) is a poorly characterized class A G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) encoded by the *GPR169* gene in humans. It is also referred to as GPR170 in some studies and shares homology with other orphan GPCRs. GPR169 is evolutionarily conserved across species and is expressed in various tissues, including the brain, immune system, and reproductive organs, though its precise physiological role remains unclear. Studies suggest potential involvement in metabolic regulation, immune response modulation, and neuroendocrine signaling, possibly through interactions with G proteins like Gαs to regulate cyclic AMP (cAMP) pathways.
Antibodies targeting GPR169 are essential tools for elucidating its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are typically developed in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides derived from conserved regions of the receptor. They enable techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect GPR169 in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Validation often includes knockout controls to confirm specificity.
Research utilizing GPR169 antibodies has gradually expanded, linking the receptor to pathologies like cancer, obesity, and inflammatory diseases. However, its ligand and downstream signaling mechanisms remain unidentified, highlighting the need for further investigation. Commercial availability of GPR169 antibodies supports ongoing studies aiming to decode its biological significance and therapeutic potential as a drug target.
×