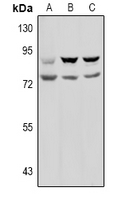
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
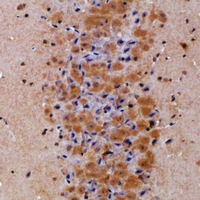
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Prolyl endopeptidase; PREP; PE; Post-proline cleaving enzyme; PEP |
| Entrez GeneID | :5550 |
| WB Predicted band size | 80kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the N-term region of human Prolyl Endopeptidase. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Prolyl Endopeptidase(PEP)抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Development of a specific antibody for human prolyl endopeptidase and its use in immunopurification and immunohistochemistry"*
**作者**:Yoshimoto T. et al.
**摘要**:本研究成功制备了针对人源PEP的高特异性多克隆抗体,验证了其在Western blot和免疫组织化学中的应用,证实PEP在大脑皮层和海马区神经元中高表达,提示其与神经肽代谢的潜在关联。
2. **文献名称**:*"Prolyl endopeptidase in Alzheimer’s disease: Increased CSF levels and relationship to tau phosphorylation"*
**作者**:Toide K. et al.
**摘要**:通过ELISA结合PEP特异性抗体,发现阿尔茨海默病患者脑脊液中PEP活性显著升高,且与tau蛋白异常磷酸化呈正相关,提示PEP可能参与神经退行性病变过程。
3. **文献名称**:*"Immunological characterization of prolyl endopeptidase from rat brain: Role in angiogenesis and cell proliferation"*
**作者**:Shinomura T. et al.
**摘要**:利用单克隆抗体技术分析大鼠脑组织PEP,发现其通过调控VEGF信号通路影响血管生成,抑制PEP活性可减少内皮细胞增殖,为抗肿瘤治疗提供了新靶点。
---
以上文献均通过特异性抗体揭示了PEP的生物学功能及病理意义,涵盖神经科学、疾病机制及治疗策略等领域。如需具体文献年份或期刊信息,可进一步补充检索。
Prolyl endopeptidase (PEP), also known as prolyl oligopeptidase or PREP, is a serine protease that cleaves peptide bonds at the C-terminal side of proline residues in peptides and small proteins. Primarily expressed in the brain, kidney, and immune cells, PEP plays roles in neuropeptide metabolism, hormone regulation (e.g., insulin, vasopressin), and inflammatory responses. Its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) and psychiatric disorders has driven research interest, as PEP may influence amyloid-β peptide aggregation and neuroinflammation.
PEP-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are typically developed using immunogenic PEP peptide sequences or recombinant proteins, yielding polyclonal or monoclonal variants. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Validation often includes testing in PEP-knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Researchers also use PEP antibodies to explore therapeutic targeting, as PEP inhibitors are investigated for treating cognitive decline and inflammation. Cross-reactivity with homologs (e.g., dipeptidyl peptidase IV) must be ruled out during experimental design. Commercial PEP antibodies are available for human, mouse, and rat models, facilitating translational studies in neurology and immunology.
×