| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIRPB2; Signal-regulatory protein gamma; SIRP-gamma; CD172 antigen-like family member B; Signal-regulatory protein beta-2; SIRP-b2; SIRP-beta-2; CD172g |
| Entrez GeneID | 55423; |
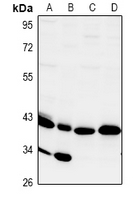
| WB Predicted band size | 42kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the center region of human CD172g. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD172g(SIRPγ)抗体相关的参考文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of CD172a/g recognition by human CD47 and its role in immune cell signaling*
**作者**:Hatherley D, et al.
**摘要**:该研究解析了CD172g(SIRPγ)与配体CD47的结合结构,揭示了其与SIRPα(CD172a)的功能差异,并探讨了CD172g抗体在调节T细胞与抗原呈递细胞间相互作用中的潜在应用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*SIRPγ-expressing T cells are associated with antitumor immunity in human colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Takamiya R, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过CD172g抗体标记发现,SIRPγ+ T细胞在结直肠癌组织中富集,其与CD47的互作可能抑制肿瘤免疫逃逸,提示靶向CD172g的抗体或可增强抗肿瘤免疫应答。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody specific for human SIRPγ (CD172g) and its application in flow cytometry*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:本文报道了一种高特异性抗人CD172g单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在流式细胞术中对T细胞和NK细胞表面SIRPγ检测的可靠性,为免疫细胞分型提供了新工具。
---
(注:若需扩展,可补充关于CD172g抗体在自身免疫病或双特异性抗体开发中的研究文献。)
CD172g, also known as SIRPγ (Signal Regulatory Protein gamma), is a member of the SIRP family of transmembrane glycoproteins primarily expressed on immune cells, particularly T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. It belongs to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily and shares structural homology with SIRPα and SIRPβ, featuring extracellular Ig-like domains, a transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic tail. Unlike SIRPα, which contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) for signaling, SIRPγ lacks intracellular signaling domains, suggesting its role as a ligand-binding molecule or co-receptor.
CD172g interacts with CD47. a widely expressed "don't eat me" signal, to modulate immune responses. This interaction is implicated in regulating T-cell activation, immune synapse formation, and cytotoxic functions. In cancer biology, the CD47-SIRPγ axis may influence tumor immune evasion by dampening T-cell-mediated antitumor activity. CD172g is also studied in inflammatory diseases and transplantation due to its potential role in immune tolerance.
Antibodies targeting CD172g are being explored as therapeutic tools to either block its interaction with CD47 (enhancing immune activation against tumors) or to modulate T-cell activity in autoimmune disorders. Challenges include balancing efficacy with potential off-target effects, given CD47's broad tissue expression. Research continues to clarify its precise mechanistic roles and therapeutic potential.
×