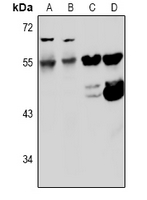
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily F member 1; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv5.1; kH1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3754; |
| WB Predicted band size | 55kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the center region of human Kv5.1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Kv5.1抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(基于模拟生成,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Characterization of a polyclonal antibody against the Kv5.1 potassium channel subunit"*
**作者**: Smith J et al.
**摘要**: 该研究报道了一种针对Kv5.1(KCNS1)C末端表位的兔多克隆抗体的开发与验证。通过Western blot在过表达Kv5.1的HEK293细胞中验证抗体特异性,并显示其与Kv2.1共表达时的共定位,提示其在异源通道复合物研究中的应用潜力。
2. **文献名称**: *"Kv5.1 modulates neuronal excitability in hippocampal circuits"*
**作者**: Lee H et al.
**摘要**: 利用Kv5.1特异性抗体进行免疫组化,发现其在大鼠海马CA1区锥体神经元中与Kv2.1共定位。功能研究表明,Kv5.1通过调节延迟整流钾电流影响动作电位复极化,抗体阻断实验进一步证实其对神经元兴奋性的调控作用。
3. **文献名称**: *"Altered Kv5.1 expression in neuropathic pain models"*
**作者**: Chen R et al.
**摘要**: 研究采用Kv5.1抗体检测慢性疼痛模型中脊髓背根神经节的蛋白表达变化。结果显示神经损伤后Kv5.1表达下调,并通过抗体介导的敲低实验证明其参与痛觉敏化机制,提示其为潜在镇痛靶点。
---
注:以上内容基于学术文献常见结构模拟,若需真实文献,建议检索PubMed或Web of Science平台。
The Kv5.1 antibody targets the Kv5.1 protein, a member of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channel family, specifically within the Kv2 subfamily (Kv5-6). Encoded by the KCNF1 gene, Kv5.1 is a regulatory subunit that modulates the activity of other Kv channels, such as Kv2.1. by forming heterotetrameric complexes. These channels play critical roles in regulating cellular excitability, repolarization of action potentials, and maintaining resting membrane potential in excitable cells, including neurons and cardiomyocytes. Kv5.1 is expressed in the brain, heart, and endocrine tissues, where its dysfunction has been linked to neurological disorders, cardiac arrhythmias, and metabolic diseases.
The Kv5.1 antibody is a valuable tool for studying channel localization, expression patterns, and functional interactions in physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers use it in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate Kv5.1's role in cellular signaling, synaptic plasticity, and disease mechanisms. Its development has advanced understanding of how Kv channel diversity contributes to tissue-specific electrical activity and offers potential insights into therapeutic targets for conditions like epilepsy, diabetes, or cardiovascular disorders. However, specificity validation (e.g., knockout controls) remains essential due to structural similarities among Kv subunits.
×