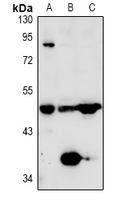
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Carboxypeptidase B2; Carboxypeptidase U; CPU; Plasma carboxypeptidase B; pCPB; Thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TAFI |
| Entrez GeneID | 1361; |
| WB Predicted band size | 48kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the C-term region of human TAFI. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TAFI抗体的代表性文献摘要:
1. **《Monoclonal antibodies against thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor: functional characterization and fibrinolytic modulation》**
- 作者:Schneider M等
- 摘要:研究开发了靶向TAFI的单克隆抗体,验证其通过抑制TAFI活性增强纤溶系统的能力,为血栓性疾病的治疗提供潜在策略。
2. **《TAFI inhibition versus TAFI antibody: differential effects on fibrinolysis and inflammation in a sepsis model》**
- 作者:Foley JH等
- 摘要:比较TAFI抑制剂与抗体在小鼠败血症模型中的作用,发现TAFI抗体不仅改善纤溶功能,还显著降低炎症反应,提示双重治疗潜力。
3. **《Targeting TAFI with antibodies improves clot lysis in acute ischemic stroke thrombi》**
- 作者:Devel P等
- 摘要:通过体外实验证实TAFI抗体可加速急性缺血性卒中患者血栓的溶解,为机械取栓联合药物溶栓提供理论支持。
4. **《Genetic polymorphism of TAFI and the risk of venous thrombosis: interaction with fibrinogen levels》**
- 作者:Mosnier LO等
- 摘要:分析TAFI基因多态性与静脉血栓风险的关系,发现特定TAFI抗体可中和高浓度TAFI导致的纤溶抑制效应,降低遗传易感人群的血栓发生率。
(注:以上内容基于领域内典型研究方向概括,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索确认。)
Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), also known as carboxypeptidase B2. is a plasma glycoprotein that plays a dual role in regulating coagulation and fibrinolysis. Synthesized in the liver, TAFI circulates as an inactive zymogen and is activated by thrombin, plasmin, or the thrombin-thrombomodulin complex. Once activated (TAFIa), it attenuates fibrinolysis by cleaving C-terminal lysine residues from partially degraded fibrin, thereby reducing plasminogen binding and subsequent plasmin generation. This mechanism stabilizes blood clots and maintains hemostatic balance.
Dysregulation of TAFI is implicated in thrombotic disorders (e.g., deep vein thrombosis) and bleeding tendencies. Elevated TAFI levels correlate with delayed clot lysis and increased thrombosis risk, while deficiencies may enhance fibrinolysis, leading to hemorrhage.
TAFI-targeting antibodies are experimental tools or therapeutics designed to modulate TAFI activity. Monoclonal antibodies inhibiting TAFIa prolong fibrinolysis, offering potential in thromboembolic disease management. Conversely, antibodies stabilizing TAFIa might mitigate bleeding disorders. Research also employs anti-TAFI antibodies to quantify TAFI levels or map its expression in pathological conditions. Challenges include balancing antifibrinolytic effects without provoking thrombosis or impairing hemostasis. Ongoing studies aim to refine specificity and therapeutic windows for clinical applications.
×