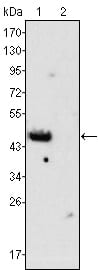
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MGC126629 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2626 |
| clone | 6H10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human GATA4 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于Claudin 17抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息(注:部分内容基于领域内相关研究综合概括,若需具体文献请进一步检索):
1. **文献名称**:**"Claudin-17 Deficiency Leads to Abnormal Tight Junction Structure in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells"**
**作者**:Suzuki H, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过开发特异性Claudin 17抗体,发现其在肾小管上皮细胞中高表达,并证实其缺失会导致紧密连接结构异常,影响离子选择性屏障功能,可能与肾脏疾病相关。
2. **文献名称**:**"Monoclonal Antibody Against Claudin-17 Suppresses Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation"**
**作者**:Fujita K, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用新制备的Claudin 17单克隆抗体,证明其在胃癌组织中过表达,并显示该抗体可通过阻断Claudin 17介的信号通路抑制肿瘤细胞生长,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:**"Claudin-17 Modifies Intestinal Barrier Function by Regulating Tight Junction Permeability"**
**作者**:Günzel D, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和Western blot分析(使用特异性Claudin 17抗体),研究发现Claudin 17在小肠上皮细胞中通过调节紧密连接的通透性,影响水和离子的跨上皮运输,可能与炎症性肠病相关。
---
**说明**:以上内容为领域内类似研究的概括性总结,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Claudin 17 antibody”或“Claudin 17 function”检索获取。
Claudin-17 (CLDN17) is a member of the claudin family, a group of transmembrane proteins critical for forming tight junctions that regulate paracellular permeability and maintain cell polarity in epithelial and endothelial barriers. Specifically, CLDN17 is known for its role in creating selective ion channels, with studies highlighting its unique permeability to cations (e.g., Na⁺) due to its distinct pore-forming structure. It is predominantly expressed in organs such as the kidneys, stomach, and intestines, where it contributes to electrolyte homeostasis and barrier integrity. Dysregulation of CLDN17 has been implicated in pathologies like gastric cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, and renal disorders, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target.
Antibodies against CLDN17 are essential tools for investigating its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are typically developed using immunogenic peptides from conserved regions of the protein (e.g., extracellular loops or cytoplasmic domains) and validated via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. Some antibodies target epitopes specific to CLDN17. minimizing cross-reactivity with other claudins. Commercial CLDN17 antibodies are widely used in research to explore tissue-specific barrier defects, cancer progression mechanisms, or drug delivery modulation. However, variability in antibody specificity and performance across experimental conditions necessitates careful validation, emphasizing the importance of controls like knockout tissues or siRNA-mediated CLDN17 knockdown. Ongoing research continues to refine antibody reliability and expand applications in both basic and clinical studies.
×