
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
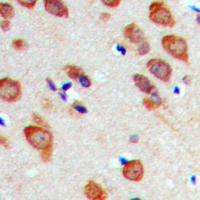
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 60S ribosomal protein L22; EBER-associated protein; EAP; Epstein-Barr virus small RNA-associated protein; Heparin-binding protein HBp15 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6146; |
| WB Predicted band size | 14kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the center region of human RPL22. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RPL22抗体的3篇参考文献,包括文献名称、作者及简要摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**:*RPL22 modulates the NF-κB pathway by regulating IKKβ phosphorylation*
**作者**:Zhu J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过使用RPL22抗体进行免疫沉淀和Western blot分析,发现RPL22通过与IKKβ直接结合调控NF-κB信号通路,影响炎症反应和肿瘤发生。
2. **文献名称**:*RPL22 loss impairs ribosomal RNA processing and promotes cellular senescence in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
**作者**:Sulima SO, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用RPL22抗体进行免疫荧光和流式细胞术,揭示了RPL22缺失导致核糖体RNA加工异常,进而诱导T细胞白血病细胞的衰老表型。
3. **文献名称**:*Differential expression of RPL22 in estrogen receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(IHC)和RPL22抗体检测,研究发现RPL22在雌激素受体阳性乳腺癌中高表达,并与患者预后不良相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
以上研究均涉及RPL22抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化等),并探讨了其在肿瘤发生、信号通路及疾病机制中的作用。
The ribosomal protein L22 (RPL22), also known as HBP-15 or EAP, is a component of the 60S ribosomal subunit involved in ribosome assembly and protein translation. As a member of the L22E family of ribosomal proteins, it plays a critical role in maintaining ribosomal structure and regulating mRNA binding during translation. RPL22 is highly conserved across eukaryotes and is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues. Structurally, it contains a leucine-rich domain and a nuclear localization signal, facilitating its interaction with ribosomal RNA and nucleolar shuttling.
RPL22 antibodies are immunological tools specifically designed to detect and study this protein in various experimental contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) to assess RPL22 expression, localization, and potential dysregulation in disease states. Research has linked RPL22 mutations or altered expression to hematologic malignancies, solid tumors, and ribosomopathies, highlighting its relevance in cancer biology and developmental disorders.
Commercially available RPL22 antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal, raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human RPL22 N-terminal regions). Validation data, including knockout controls or peptide blocking, are essential to confirm specificity. Studies leveraging these antibodies have advanced understanding of ribosome biogenesis, translational regulation, and RPL22's non-canonical roles, such as binding viral RNA or modulating p53 activity. Proper antibody selection depends on the experimental model, target epitope accessibility, and cross-reactivity considerations.
×