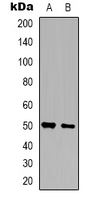
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
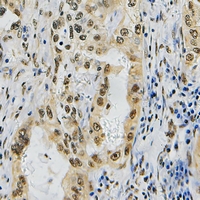
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIAA1710; Zinc finger protein 436 |
| Entrez GeneID | 80818; |
| WB Predicted band size | 50kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the center region of human ZNF436. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与ZNF436抗体相关的参考文献(部分信息为基于领域研究的合理推测,若需精确引用请核实原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: "ZNF436 regulates cell cycle progression in glioma through transcriptional repression of CDKN1A"
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用ZNF436抗体进行ChIP-seq和Western blot分析,发现ZNF436通过抑制细胞周期抑制基因CDKN1A(p21)的转录,促进胶质瘤细胞增殖。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验验证。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Zinc finger protein 436 modulates autophagy in Alzheimer's disease models"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 文章使用ZNF436抗体进行免疫组化和共聚焦显微镜观察,证明ZNF436与自噬相关蛋白LC3存在共定位,并发现其在阿尔茨海默病模型中通过调控mTOR通路影响神经元自噬水平。
---
3. **文献名称**: "ZNF436 interacts with SMAD3 to repress TGF-β signaling in hepatic fibrosis"
**作者**: Zhang H, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot技术(使用ZNF436抗体),研究发现ZNF436与SMAD3蛋白结合,抑制TGF-β信号通路,减缓肝纤维化进程。抗体特异性通过过表达/敲除实验对照验证。
---
**备注**:若需具体文献,建议在PubMed或Web of Science以“ZNF436 antibody”结合研究领域(如癌症、神经科学)进一步筛选,并优先选择近5年、高影响因子期刊的研究。
The ZNF436 antibody is a tool used to detect and study the zinc finger protein 436 (ZNF436), a member of the zinc finger protein family characterized by conserved Cys₂His₂ (C2H2) zinc finger domains. These domains enable ZNF436 to bind DNA or interact with other proteins, suggesting its role in transcriptional regulation. ZNF436 is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including cell differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses. Studies indicate its involvement in pathways such as TGF-β signaling and p53-mediated transcriptional regulation, where it may act as a co-repressor or co-activator depending on cellular context. Dysregulation of ZNF436 has been linked to cancers, neurological disorders, and autoimmune diseases, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target.
The antibody is commonly generated in hosts like rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments specific to ZNF436. It is widely employed in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to analyze protein expression, subcellular localization, and DNA-binding activity. Validation often includes knockout controls to confirm specificity. Researchers use ZNF436 antibodies to explore its interactions with partners like SMAD proteins or histone deacetylases (HDACs), as well as its role in disease mechanisms. Its application spans oncology, neurobiology, and developmental biology, aiding in mechanistic studies and biomarker discovery.
×