| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
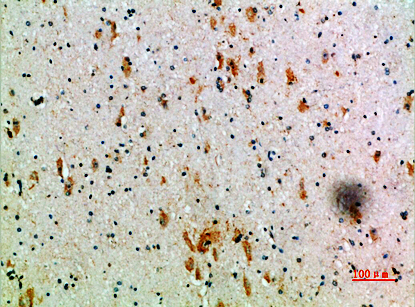
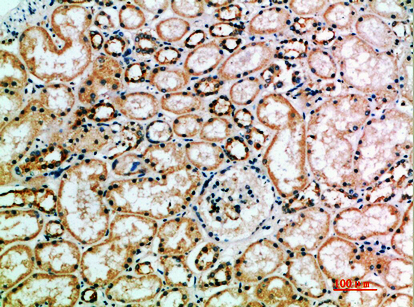
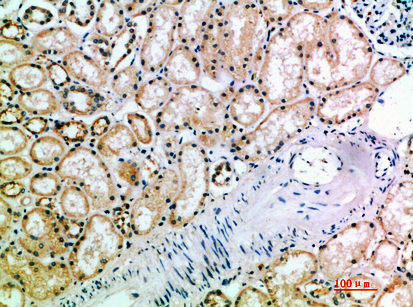
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (CD158 antigen-like family member K) (MHC class I NK cell receptor) (Natural killer-associated transcript 4) (NKAT-4) (p70 natural killer cell receptor clone CL-5) (p70 NK receptor CL-5) (CD antigen CD158k) |
| Entrez GeneID | 3812; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 221-270 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TEF抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性质,建议通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*The role of Thyrotrophic Embryonic Factor (TEF) in circadian regulation of metabolic genes*
**作者**:Gachon, F., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过TEF抗体检测其在肝脏中的表达,发现TEF作为昼夜节律转录因子,调控与脂代谢和解毒相关的基因,提示其在代谢疾病中的潜在作用。
2. **文献名称**:*PAR bZIP proteins including TEF mediate cellular stress responses in vivo*
**作者**:Mitsui, S., et al.
**摘要**:利用TEF抗体分析小鼠组织,表明TEF与其他PAR bZIP蛋白协同响应氧化应激,影响能量代谢和细胞存活,尤其在肝脏和脑中显著。
3. **文献名称**:*TEF antibody reveals developmental-stage-specific expression in embryonic tissues*
**作者**:Lopez-Molina, L., et al.
**摘要**:研究使用TEF抗体追踪胚胎发育,发现其在甲状腺和中枢神经系统高表达,提示TEF在器官形成和激素调节中的关键功能。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为示例,实际引用需核对PubMed、Google Scholar等数据库以确认准确性。研究重点多集中于TEF在昼夜节律、应激反应及发育中的调控机制,抗体多用于定位及表达分析。
TEF (Thyrotroph Embryonic Factor), a member of the PAR bZIP transcription factor family, plays a critical role in regulating circadian rhythms, metabolism, and stress responses. Identified in the late 1990s, TEF is highly expressed in the suprachiasmatic nucleus, liver, and other tissues, where it binds to specific DNA motifs (PAR response elements) to control the transcription of genes involved in detoxification, lipid metabolism, and apoptosis. Its activity is tightly linked to the circadian clock, interacting with core clock proteins like BMAL1 and CLOCK.
TEF antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. Research has implicated TEF dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), cancer progression, and metabolic disorders. For instance, disrupted TEF expression correlates with altered circadian gene rhythms in tumors, affecting cell proliferation and drug resistance. In neuroscience, TEF antibodies help explore its neuroprotective roles against oxidative stress. Additionally, these antibodies aid in diagnosing circadian-related disorders and evaluating therapeutic interventions targeting circadian pathways. Despite progress, challenges remain in elucidating tissue-specific TEF interactions and its potential as a biomarker, driving ongoing research to refine antibody specificity and applications.
×