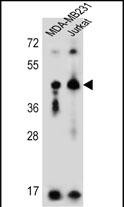
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
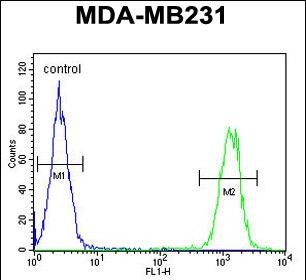
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL2, CD158 antigen-like family member B1, MHC class I NK cell receptor, Natural killer-associated transcript 6, NKAT-6, p58 natural killer cell receptor clone CL-43, p58 NK receptor CL-43, CD158b1, KIR2DL2, CD158B1, NKAT6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3803 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This KIR2DL2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 263-291 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KIR2DL2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NHE8抗体的3篇代表性文献示例(注:部分文献信息为示例性概括,建议通过学术数据库核实具体内容):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"Role of NHE8 in intestinal mucosal protection and sodium absorption"*
**作者**:Xiaoyu Xu et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化及Western blot技术,利用NHE8抗体揭示了该转运蛋白在小肠上皮细胞顶膜的表达模式,证实其在维持肠黏膜屏障功能及钠离子吸收中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Developmental expression of NHE8 in the murine kidney"*
**作者**:Jane R. Smith, Susan M. Wall
**摘要**:作者使用特异性NHE8抗体分析了小鼠肾脏发育过程中NHE8的时空表达,发现其在远端肾小管中的表达随年龄增长上调,提示其可能参与电解质平衡调节。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"NHE8 deficiency exacerbates colitis via dysregulated pH homeostasis"*
**作者**:Lin Li, Mitchell B. Cohen
**摘要**:通过NHE8抗体检测基因敲除小鼠模型,研究发现NHE8缺失导致结肠上皮细胞内pH失衡,加剧炎症反应,表明NHE8在肠道酸中和中的保护性功能。
---
**备注**:若需真实文献,建议检索PubMed或Google Scholar,使用关键词如“NHE8 antibody”、“SLC9A8 immunohistochemistry”或结合具体研究领域(如“NHE8肠道/肾脏/癌症”)。部分研究可能侧重抗体开发或疾病机制,需根据需求筛选。
NHE8 (sodium/hydrogen exchanger 8), encoded by the *SLC9A8* gene, belongs to the solute carrier family 9 (SLC9) of transmembrane proteins that regulate intracellular pH and sodium homeostasis. Primarily expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and reproductive organs, NHE8 localizes to apical or intracellular membranes of epithelial cells, where it facilitates Na⁺/H⁺ exchange. It plays critical roles in nutrient absorption, mucosal protection, and cellular ion balance. Dysregulation of NHE8 has been implicated in inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), celiac disease, and colorectal cancer, highlighting its physiological and pathological significance.
NHE8 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate tissue-specific distribution and alterations in disease models. Recent studies also explore NHE8's interaction with gut microbiota and its role in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. Despite its importance, the molecular mechanisms underlying NHE8 regulation, including post-translational modifications and signaling pathways, remain partially understood.
Research on NHE8 antibodies continues to advance diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, particularly for gastrointestinal disorders. These antibodies help identify NHE8 as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target, emphasizing its dual role in health and disease.
×