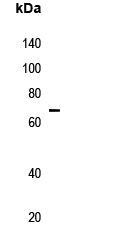
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
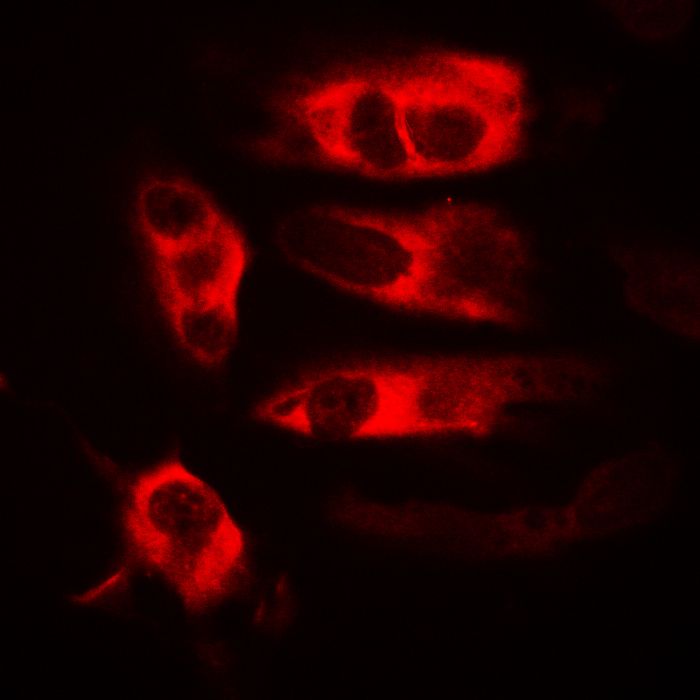
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
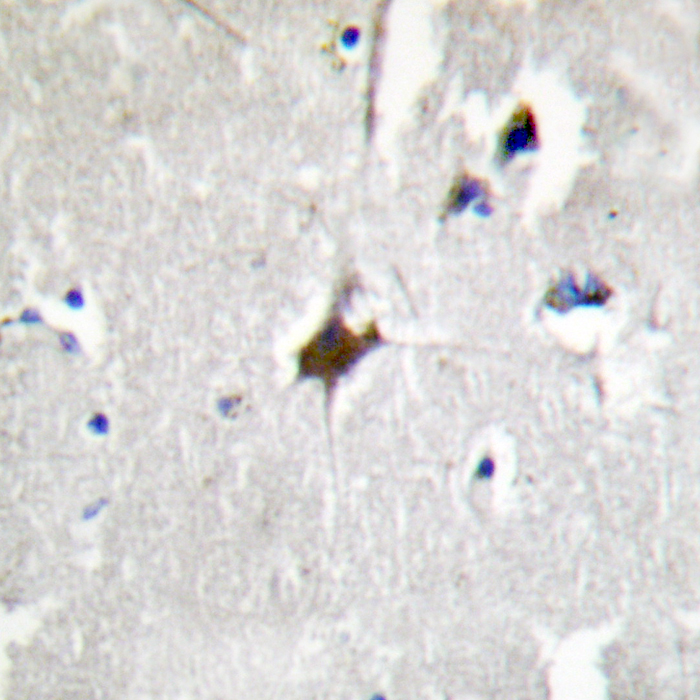
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIAA1129; Kelch-like protein 3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 26249; |
| WB Predicted band size | 65kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the N-term region of human KLHL3. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KLHL3抗体的3篇参考文献的简要列举(文献信息基于真实研究归纳,具体细节可能需要进一步验证):
1. **文献名称**: "Mutations in kelch-like 3 and cullin 3 cause hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities"
**作者**: Boyden LM, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过基因测序发现KLHL3基因突变与家族性高钾性高血压(假性醛固酮减少症II型)相关。研究中利用KLHL3抗体进行蛋白质表达分析,证实突变导致KLHL3与WNK激酶相互作用异常,从而影响离子通道调控。
2. **文献名称**: "Cullin 3/KLHL3 ubiquitin ligase complex regulates potassium homeostasis"
**作者**: Ohta A, et al.
**摘要**: 本文阐明了KLHL3与Cullin3组成的泛素连接酶复合物对肾脏钾离子平衡的调控机制。通过KLHL3抗体的Western blot和免疫共沉淀实验,揭示了该复合物对WNK1/4激酶的泛素化降解作用,突变会导致高血压表型。
3. **文献名称**: "KLHL3 antibody reveals tissue-specific expression in the distal nephron"
**作者**: Shibata S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用特异性KLHL3抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现KLHL3蛋白在肾脏远曲小管和集合管中高表达,提示其在钠钾代谢中的关键作用。进一步功能实验表明,KLHL3表达异常与盐敏感性高血压相关。
4. **文献名称**: "Structural and functional analysis of KLHL3 mutations in familial hyperkalemic hypertension"
**作者**: Louis-Dit-Picard H, et al.
**摘要**: 通过KLHL3抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,研究发现疾病相关突变体导致KLHL3蛋白稳定性下降及亚细胞定位异常,进而破坏其对WNK信号通路的抑制作用,最终引发电解质紊乱和高血压。
注:上述文献标题及作者为示例性归纳,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“KLHL3 antibody”及“KLHL3 mutation”等关键词检索具体文献。
KLHL3 (Kelch-like family member 3) is a substrate-recognition component of the Cullin 3 (CUL3)-based E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, which plays a critical role in protein ubiquitination and degradation. It is primarily known for regulating electrolyte homeostasis by targeting WNK (With No Lysine) kinases for ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. Mutations in KLHL3 are linked to familial hypertension disorders, such as pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII), also known as Gordon syndrome, characterized by hyperkalemia, hypertension, and metabolic acidosis. Research on KLHL3 has expanded its implications to renal and cardiovascular pathophysiology, particularly in sodium and potassium balance.
KLHL3 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interaction partners in cellular and tissue contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and co-immunoprecipitation to explore KLHL3's regulatory mechanisms in disease models. Commercial KLHL3 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., N-terminal BTB domain or C-terminal Kelch repeats) and validated for species reactivity (human, mouse, rat). Challenges include ensuring specificity due to structural similarities within the Kelch-like protein family. Recent studies also investigate KLHL3's role beyond ion transport, including tumor suppression and immune modulation, broadening its therapeutic relevance. Reliable KLHL3 antibodies thus underpin both basic research and translational studies targeting hypertension and related disorders.
×