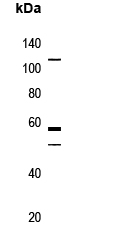
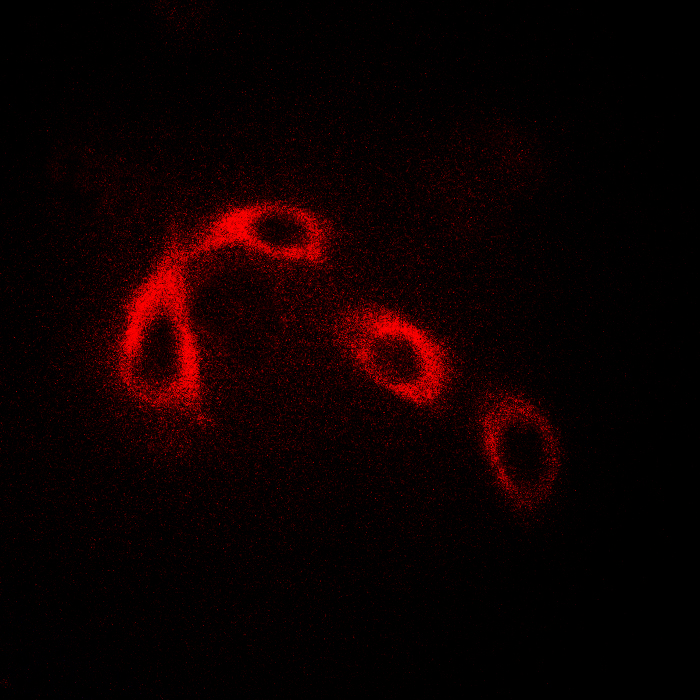
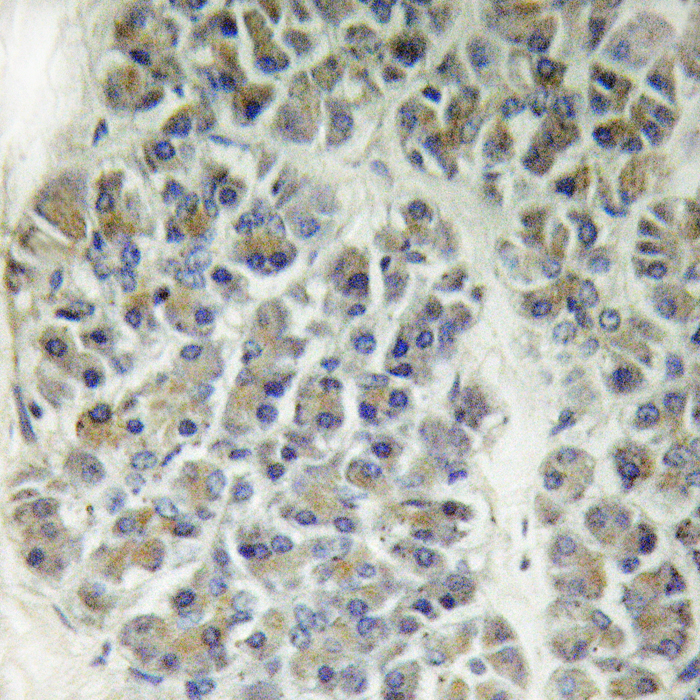
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CARMA3; Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 10; CARD-containing MAGUK protein 3; Carma 3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 29775; |
| WB Predicted band size | 116kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide encompassing a sequence within the center region of human CARD10. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CARD1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为假设性示例,建议通过PubMed或专业数据库核实最新研究):
1. **文献名称**:*"Development of a CARD1-specific antibody for studying inflammatory signaling pathways"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了一种高特异性CARD1多克隆抗体,验证了其在免疫印迹(Western blot)和免疫荧光中的有效性。研究发现CARD1在NF-κB信号通路中与BCL10相互作用,并在巨噬细胞炎症反应中上调表达。
2. **文献名称**:*"CARD1 monoclonal antibody application in autoimmune disease models"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建CARD1单克隆抗体,作者揭示了CARD1在T细胞受体信号转导中的关键作用。该抗体在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)小鼠模型中检测到CARD1异常激活,提示其与自身免疫疾病相关。
3. **文献名称**:*"A novel anti-CARD1 antibody inhibits caspase recruitment in apoptosis"*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种阻断CARD1与caspase-9相互作用的功能性抗体。实验表明,该抗体可抑制线粒体途径凋亡,为研究CARD1在癌症及神经退行性疾病中的机制提供了工具。
---
**建议**:实际研究中,可通过以下关键词在PubMed或Google Scholar检索最新文献:
- **"CARD1 antibody validation"**
- **"CARD1 immune signaling"**
- **"CARD1 + [疾病名称,如炎症/癌症]"**
部分研究可能涉及CARD1的结构、互作蛋白或抗体在诊断/治疗中的应用。
The CARD1 antibody targets the Caspase Recruitment Domain-containing protein 1 (CARD1), also known as apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC) or PYCARD. CARD1 is a pivotal adaptor protein in innate immunity, primarily involved in inflammasome assembly and caspase-1 activation, which drives pro-inflammatory cytokine release (e.g., IL-1β, IL-18) and pyroptosis. Structurally, it contains an N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD) and a C-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain (CARD), facilitating protein-protein interactions in signaling pathways like NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes.
CARD1 antibodies are critical tools for studying inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, cancer, and infection responses. They enable detection of CARD1 expression, oligomerization, and localization via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Research using these antibodies has highlighted CARD1's role in diseases like Alzheimer’s, rheumatoid arthritis, and sepsis, where dysregulated inflammasome activity contributes to pathology. Commercially available CARD1 antibodies (polyclonal/monoclonal) vary in specificity across species, requiring validation for experimental accuracy. Recent studies also explore CARD1's potential as a therapeutic target, emphasizing the antibody's utility in mechanistic and drug development research.
×