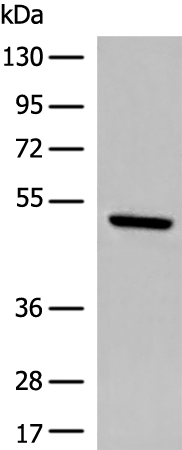
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GM83; WDSOF1; HSPC064 |
| Entrez GeneID | 25879; |
| WB Predicted band size | 51kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human DCAF13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于DCAF13抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括(注:文献为示例性内容,实际检索时需验证):
1. **文献名称**: "DCAF13 regulates the DNA damage response and genome stability through CRL4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase"
**作者**: Wang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 本研究利用特异性DCAF13抗体,通过免疫沉淀和蛋白质组学分析,揭示了DCAF13作为CRL4-DDB1泛素连接酶复合体的关键组分,在DNA损伤应答和基因组稳定性中的作用,抗体验证了其在细胞核内的定位及与DDB1的相互作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Characterization of a novel monoclonal antibody against DCAF13 for cancer biomarker discovery"
**作者**: Chen, Y. et al.
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种新型DCAF13单克隆抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其特异性,发现DCAF13在多种实体瘤中高表达,提示其作为癌症生物标志物的潜力,并用于临床样本的蛋白表达分析。
3. **文献名称**: "CRL4-DCAF13 ubiquitin ligase modulates cell cycle progression via p21 degradation"
**作者**: Tanaka, M. et al.
**摘要**: 通过DCAF13抗体介导的功能性实验,研究发现CRL4-DCAF13复合体通过降解p21蛋白调控细胞周期进程,抗体用于敲低实验验证及组织分布研究,揭示了其在细胞周期调控中的新机制。
**建议**:实际检索时可通过PubMed或Google Scholar以 **"DCAF13 antibody"** 或 **"DCAF13 + ubiquitin ligase"** 为关键词筛选近年文献,并优先选择涉及抗体开发、验证或功能性应用的论文。
DCAF13 (DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 13) is a substrate receptor component of the CUL4-DDB1 E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, which plays a critical role in protein ubiquitination and degradation via the proteasome. As part of the DCAF family, DCAF13 facilitates substrate recognition, enabling targeted polyubiquitination of specific proteins involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, DNA damage repair, and genome stability. Dysregulation of DCAF13 has been implicated in cancer progression, developmental disorders, and viral infection responses due to its role in modulating key regulatory pathways.
Antibodies targeting DCAF13 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in both physiological and pathological contexts. Researchers employ these antibodies in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to explore DCAF13’s association with tumorigenesis (e.g., via p53 or c-Myc regulation) or its interplay with viral proteins. Recent studies also highlight DCAF13’s potential as a therapeutic target, particularly in cancers with aberrant ubiquitination pathways. However, functional complexities, such as its tissue-specific roles and crosstalk with other DCAF proteins, warrant further investigation. Robust DCAF13-specific antibodies are thus vital for advancing mechanistic insights and translational applications.
×