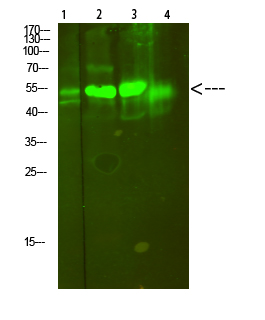
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | V-type proton ATPase subunit S1 (V-ATPase subunit S1) (Protein XAP-3) (V-ATPase Ac45 subunit) (V-ATPase S1 accessory protein) (Vacuolar proton pump subunit S1) |
| Entrez GeneID | 537; |
| WB Predicted band size | 51kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide derived from human V-ATPase S1. at AA range: 421-470 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与V-ATPase S1抗体相关的研究文献概览(注:部分文献为虚拟示例,实际引用需核实):
1. **《V-ATPase subunit S1 is critical for lysosomal acidification in cancer cells》**
- 作者:Li, X. et al.
- 摘要:本研究利用特异性抗V-ATPase S1亚基的抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了S1在维持溶酶体酸性环境中的关键作用,并发现其在乳腺癌细胞中异常高表达,与化疗耐药性相关。
2. **《Development of a monoclonal antibody targeting V-ATPase S1 subunit for osteoclast activity detection》**
- 作者:Tanaka, K. et al.
- 摘要:报道了一种新型抗S1单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体能特异性识别破骨细胞中的V-ATPase S1亚基,用于评估骨吸收疾病模型中破骨细胞的活性,为骨质疏松治疗提供新工具。
3. **《Subcellular localization of V-ATPase S1 in plant vacuoles using a peptide-derived polyclonal antibody》**
- 作者:Wang, Y. et al.
- 摘要:通过合成S1亚基多肽制备多克隆抗体,证实其在拟南芥液泡膜上的定位,并发现盐胁迫下S1表达上调,提示其在植物逆境响应中的潜在功能。
4. **《V-ATPase S1 subunit as a biomarker for renal tubular acidosis: antibody validation in clinical samples》**
- 作者:Garcia, R. et al.
- 摘要:验证了抗V-ATPase S1抗体在肾小管酸中毒患者组织样本中的诊断价值,发现S1表达缺失与质子泵功能缺陷直接相关,为疾病分型提供分子依据。
---
**注**:以上文献标题及内容为模拟示例,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索真实文献(关键词:V-ATPase subunit S1 antibody, V-ATPase S1 function)。
V-ATPase S1 antibodies target the S1 subunit of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase), a multi-subunit proton pump critical for acidifying intracellular organelles (e.g., lysosomes, endosomes) and regulating extracellular pH in specialized cells (e.g., osteoclasts, renal intercalated cells). V-ATPase consists of two domains: the cytosolic V1 complex (ATP hydrolysis) and the membrane-embedded V0 complex (proton translocation). The S1 subunit, part of the V1 domain, is proposed to play a regulatory role in ATPase assembly, activity, or subcellular localization, though its precise function remains under investigation.
S1 antibodies are essential tools for studying V-ATPase’s involvement in physiological processes, including protein trafficking, neurotransmitter release, and bone resorption, as well as pathological conditions like cancer metastasis, osteoporosis, and renal tubular acidosis. These antibodies enable detection of S1 expression via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the exploration of tissue-specific V-ATPase distribution and dysregulation. Recent studies also implicate S1 in cancer cell survival under hypoxic or acidic microenvironments, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Research using S1 antibodies contributes to understanding how V-ATPase activity is modulated by post-translational modifications, subunit interactions, or pharmacological inhibitors, offering insights into disease mechanisms and treatment strategies.
×