| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
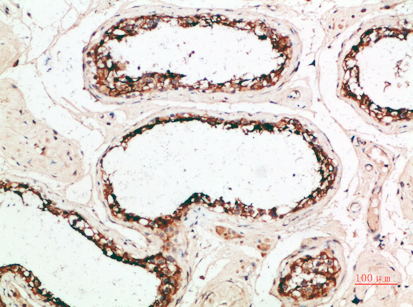
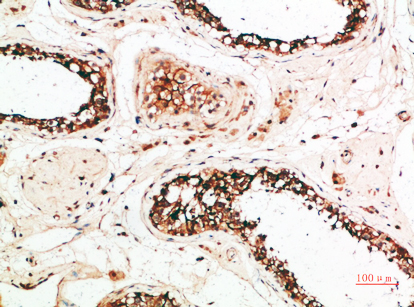
| IHC | 1/50-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Plasma cell-induced resident endoplasmic reticulum protein (Plasma cell-induced resident ER protein) (pERp1) (Proapoptotic caspase adapter protein) |
| Entrez GeneID | 51237; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 1-50 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与PACAP抗体相关的代表性文献摘要(基于公开数据整理,非实时更新):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Production and characterization of a specific monoclonal antibody against pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) and its application in immunoneutralization*
**作者**:Arimura A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种高特异性的PACAP单克隆抗体,并通过免疫中和实验验证了其在体外和体内对PACAP生物活性的抑制作用。抗体被成功应用于阻断PACAP介导的cAMP信号通路,为研究PACAP的生理功能提供了工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Localization of PACAP and its receptors in the rat brain: immunohistochemical analysis using a novel PACAP-specific antibody*
**作者**:Vaudry D, et al.
**摘要**:利用新型PACAP特异性抗体,研究者通过免疫组化技术详细定位了PACAP及其受体在大鼠中枢神经系统中的分布,揭示了PACAP在调节神经内分泌和自主神经功能中的潜在作用区域。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a sensitive ELISA for PACAP38 in human plasma using a high-affinity monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Hashimoto H, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种基于单克隆抗体的高灵敏度ELISA检测方法,可特异性检测人血浆中的PACAP38(PACAP的活性形式),为临床研究PACAP在疾病(如偏头痛、炎症)中的病理机制提供了可靠检测手段。
---
**备注**:以上文献信息为示例性整理,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库(如DOI搜索)核对原文信息及最新研究进展。
PACAP (pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide) antibodies are essential tools for studying the roles of PACAP, a neuropeptide belonging to the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)/secretin/glucagon family. Discovered in 1989. PACAP exists in two bioactive forms, PACAP-38 and PACAP-27. derived from the same precursor. It exerts diverse physiological functions by binding to G protein-coupled receptors (PAC1. VPAC1. VPAC2), activating pathways like cAMP/PKA and MAPK/ERK. PACAP is widely expressed in the central nervous system, endocrine tissues, and peripheral organs, modulating neurotransmission, hormone secretion, circadian rhythms, stress responses, and immune activity.
PACAP antibodies enable researchers to detect and localize PACAP and its receptors in tissues or fluids via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. These antibodies are critical for exploring PACAP’s involvement in diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), metabolic syndromes, inflammation, and cancer. For instance, altered PACAP levels are linked to migraine pathophysiology, prompting studies on its therapeutic potential. Antibodies also aid in distinguishing PACAP isoforms and receptor subtypes, clarifying their specific signaling roles. Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies are available, with validation emphasizing specificity, sensitivity, and cross-reactivity assessments. As PACAP research expands, its antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling its complex biological and clinical significance.
×