| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
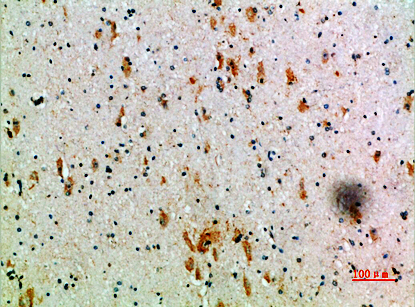
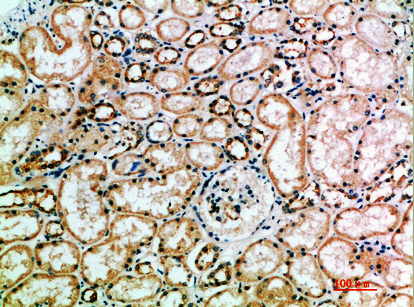
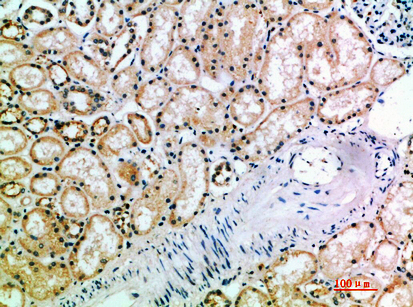
| IHC | 1/50-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (CD158 antigen-like family member K) (MHC class I NK cell receptor) (Natural killer-associated transcript 4) (NKAT-4) (p70 natural killer cell receptor clone CL-5) (p70 NK receptor CL-5) (CD antigen CD158k) |
| Entrez GeneID | 3812; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 221-270 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是与CD158k(KIR3DL2)抗体相关的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *KIR3DL2 is a coinhibitory receptor on Sezary syndrome malignant T cells*
**作者**: Poszepczynska-Guigné E, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现CD158k/KIR3DL2在皮肤T细胞淋巴瘤(如Sezary综合征)的恶性T细胞中高表达,提示其可作为疾病诊断标志物,并可能通过抗体靶向治疗抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。
2. **文献名称**: *Targeting KIR3DL2 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma by antibody-based therapies*
**作者**: Battistella M, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了一种针对KIR3DL2的单克隆抗体(IPH4102),在体外和动物模型中显示对CD158k阳性皮肤T细胞淋巴瘤细胞的高效杀伤作用,支持其进入临床试验作为免疫治疗策略。
3. **文献名称**: *KIR3DL2 regulates innate and adaptive immunity in chronic hepatitis C virus infection*
**作者**: Ahlenstiel G, et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了CD158k/KIR3DL2在慢性丙型肝炎患者NK细胞中的调控作用,发现其抗体阻断可增强NK细胞对感染肝细胞的杀伤活性,提示靶向该受体可能改善抗病毒免疫应答。
(注:若需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或学术数据库检索上述标题获取全文信息。)
CD158k, also known as KIR3DL1 (Killer-cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptor 3DL1), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the KIR family expressed primarily on natural killer (NK) cells and subsets of T lymphocytes. These receptors play a critical role in immune regulation by interacting with human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I molecules, particularly HLA-Bw4 epitopes. CD158k/KIR3DL1 functions as an inhibitory receptor, transmitting signals through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) to suppress NK cell cytotoxicity upon binding to its cognate HLA ligands. This interaction ensures self-tolerance while allowing NK cells to detect and eliminate cells with reduced HLA class I expression, a common feature of viral infections or malignancies.
CD158k antibodies are essential tools for identifying KIR3DL1-expressing cells in research and diagnostics. They are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional studies to explore KIR-HLA interactions in immune responses. Variations in KIR3DL1 genes, including allelic polymorphisms and copy number variations, influence disease susceptibility, including autoimmune disorders, viral persistence (e.g., HIV), and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcomes. Additionally, CD158k antibodies have therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy, where blocking inhibitory KIR signals may enhance NK cell-mediated tumor targeting. However, the complexity of KIR3DL1 polymorphism and ligand specificity necessitates careful antibody validation to ensure accurate detection and functional relevance in clinical applications.
×