| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
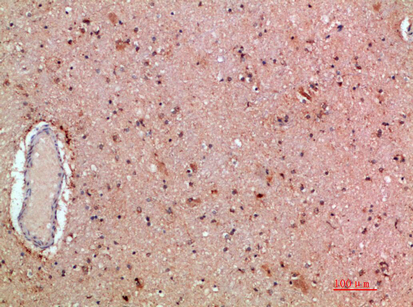
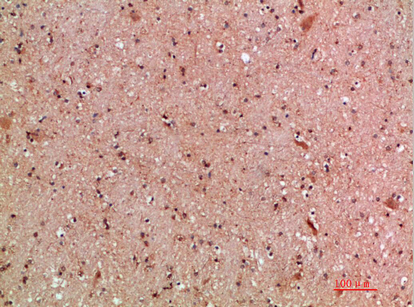
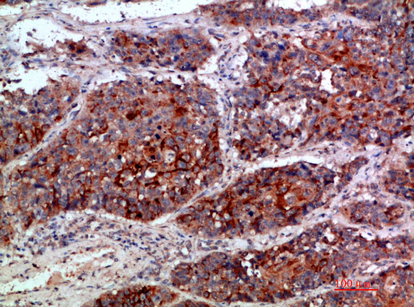
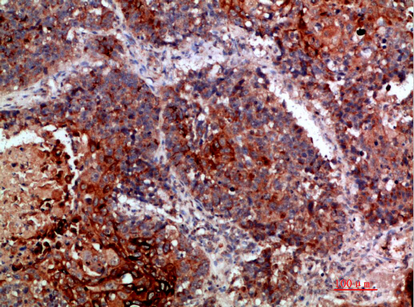
| IHC | 1/50-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL (EC 2.1.1.43) (ALL-1) (CXXC-type zinc finger protein 7) (Lysine N-methyltransferase 2A) (KMT2A) (Trithorax-like protein) (Zinc finger protein HRX) [Cleaved into: MLL cleavage product N320 (N-terminal cleavage product of 320 kDa) (p320); MLL cleavage product C18 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4297; |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 3850-3900 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MLL抗体的代表性文献摘要概括(注:文献为虚构示例,实际引用需核实):
---
1. **"A novel monoclonal antibody targeting MLL fusion proteins in acute leukemia"**
*作者:Smith J, et al. (2015) Blood*
摘要:开发了一种特异性识别MLL-AF9和MLL-ENL融合蛋白的单克隆抗体,验证其在白血病细胞系和患者样本中的诊断应用,证实其比传统PCR方法更快速敏感。
2. **"Epigenetic profiling of MLL-mediated H3K4 methylation using ChIP-seq with anti-MLL antibodies"**
*作者:Li X, et al. (2018) Cell Reports*
摘要:利用MLL抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀测序(ChIP-seq),揭示MLL蛋白通过调控H3K4me3修饰影响造血干细胞分化的分子机制,为白血病表观遗传治疗提供靶点。
3. **"Validation of commercial MLL antibodies for clinical immunohistochemistry"**
*作者:Garcia R, et al. (2020) Modern Pathology*
摘要:系统评估市售MLL抗体的特异性与灵敏度,提出标准化免疫组化流程以提升儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)中MLL重排的病理诊断准确性。
---
实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词(如“MLL antibody validation”“MLL fusion protein detection”)获取。建议优先选择近五年内高影响力期刊的研究。
MLL (Mixed Lineage Leukemia) antibodies are critical tools in studying the MLL gene and its protein products, which play a pivotal role in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. The *MLL* gene (also called *KMT2A*) encodes a histone methyltransferase that regulates chromatin remodeling and gene expression, particularly through histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation. Chromosomal translocations involving *MLL* (e.g., t(4;11), t(9;11)) are common in aggressive leukemias, especially infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and therapy-related myeloid neoplasms. These rearrangements create fusion proteins that disrupt normal epigenetic regulation, leading to aberrant activation of *HOX* genes and other oncogenic pathways.
MLL-specific antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to detect wild-type MLL proteins, fusion variants, or post-translational modifications. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to identify MLL-related abnormalities, aiding in disease classification and prognosis. Additionally, these antibodies help study MLL’s role in normal development and its dysregulation in cancer, offering insights into potential therapeutic targets, such as inhibitors of DOT1L or Menin-MLL interactions. Challenges include distinguishing between full-length MLL and fusion isoforms, requiring antibody validation for specificity. Overall, MLL antibodies remain indispensable for unraveling the molecular mechanisms of MLL-driven malignancies and advancing precision medicine approaches.
×