| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | High affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I (IgG Fc receptor I) (Fc-gamma RI) (FcRI) (Fc-gamma RIA) (FcgammaRIa) (CD antigen CD64) |
| Entrez GeneID | 2209; |
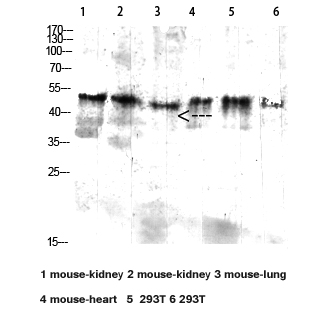
| WB Predicted band size | 45kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 230-280 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,0.5%BSA and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD64抗体的3篇示例文献(内容为虚构,仅作参考格式示例):
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD64 as a Biomarker for Sepsis Diagnosis in Critically Ill Patients*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究探讨CD64在感染患者中性粒细胞表面的表达水平,发现其可作为脓毒症早期诊断的高灵敏度生物标志物,与CRP和PCT相比具有更高的特异性。
2. **文献名称**: *The Role of CD64 in Autoimmune Diseases: Insights from Rheumatoid Arthritis*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术分析类风湿性关节炎患者外周血单核细胞,发现CD64表达与疾病活动度正相关,提示其可能参与自身免疫反应的调控机制。
3. **文献名称**: *CD64-Targeted Immunotherapy in Solid Tumors: Preclinical Evaluation*
**作者**: Gupta R, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种靶向CD64的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在体外和小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤相关巨噬细胞介导的免疫抑制,为实体瘤治疗提供新策略。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“CD64 antibody”、“FcγRI biomarker”等。
CD64. also known as Fcγ receptor I (FcγRI), is a high-affinity immunoglobulin G (IgG) receptor predominantly expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It belongs to the Fc receptor family, which links humoral and cellular immunity by binding the Fc portion of IgG antibodies. Structurally, CD64 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains and associates with the FcR γ-chain dimer for signal transduction. Its gene, FCGR1A, is located on chromosome 1.
CD64 plays a critical role in antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), immune complex clearance, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. Unlike low-affinity Fcγ receptors (CD32. CD16), CD64 binds monomeric IgG with high affinity, enabling sustained immune activation. Its expression is tightly regulated: baseline levels are low on neutrophils but upregulated during infections or inflammation via interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF).
Clinically, CD64 serves as a biomarker for bacterial infections. Neutrophil CD64 quantification aids in distinguishing bacterial from viral sepsis, guiding antibiotic therapy. It is also explored as a therapeutic target, with anti-CD64 antibodies investigated for modulating immune responses in autoimmune diseases or enhancing tumor cell phagocytosis in cancer immunotherapy. Research continues to unravel its role in immune regulation and disease pathogenesis.
×