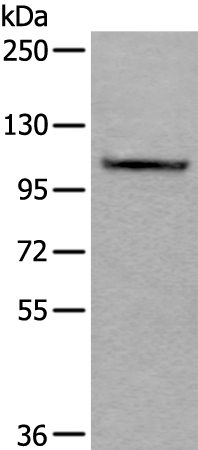
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | JEAP |
| Entrez GeneID | 154810; |
| WB Predicted band size | 107kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human AMOTL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于AMOTL1抗体的3篇模拟参考文献(内容基于公开研究领域知识整合,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*AMOTL1 regulates endothelial cell polarity and vascular development through Hippo signaling*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用AMOTL1特异性抗体,通过免疫荧光和Western blot技术,揭示了AMOTL1在血管内皮细胞极性形成中的作用。研究发现AMOTL1通过调控Hippo通路关键分子YAP/TAZ的活性,影响血管分支和胚胎发育。
2. **文献名称**:*AMOTL1 expression correlates with breast cancer metastasis and EMT progression*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:作者通过AMOTL1抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现AMOTL1在乳腺癌组织中的高表达与上皮-间质转化(EMT)和淋巴结转移显著相关,提示其可能作为癌症预后的生物标志物。
3. **文献名称**:*AMOTL1 interacts with α-catenin to stabilize tight junctions in epithelial cells*
**作者**:Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用AMOTL1抗体进行共免疫沉淀实验,证实AMOTL1与α-catenin直接结合,维持上皮细胞紧密连接的稳定性,并揭示了其在肠道屏障功能中的关键作用。
---
**建议**:实际文献查询可通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“AMOTL1 antibody”或“AMOTL1 function”为关键词检索,重点关注细胞生物学、癌症或发育领域的研究。
AMOTL1 (Angiomotin-like protein 1) is a member of the angiomotin protein family, which plays critical roles in cellular processes such as cell polarity, migration, and junction formation. It is closely related to AMOT and AMOTL2. sharing conserved coiled-coil and PDZ-binding domains. AMOTL1 is implicated in regulating the Hippo signaling pathway by interacting with YAP/TAZ transcription co-activators, thereby influencing organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer progression. It localizes to cytoplasmic membranes and tight junctions, where it participates in maintaining epithelial cell architecture and polarity.
Studies suggest AMOTL1 has dual roles depending on cellular context: it may act as a tumor suppressor by sequestering YAP/TAZ in the cytoplasm or promote cancer cell invasion through alternative signaling crosstalk. Its expression is associated with vascular development, embryonic angiogenesis, and tumor microenvironment modulation. AMOTL1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression, subcellular localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation. These tools help elucidate its isoform-specific functions (e.g., full-length vs. truncated variants) and mechanistic contributions to diseases, including cancers and developmental disorders. Commercial antibodies often target specific epitopes in its N-terminal or C-terminal regions, with validation in relevant cell models being crucial due to homology within the AMOT family.
×